Schaltungstechnik16 SpannungsreglerLängsreglerProf. Dr. Jörg Vollrath15 Rauschen |

|
Video der 16. Vorlesung 18.5.2021
|
Länge: 1:02:43 |
0:2:16 5.1 Power overview 0:4:26 5.2 Power converters 0:6:2 5.3 Need for converters 0:8:18 Load Regulation 0:11:30 Line Regulation 0:13:55 Wirkungsgrad, Efficiency 0:14:39 5.4 DC Power Distribution PC 0:19:20 5.5 Types of Converters 0:24:20 DRAM power grid 0:29:30 Power on sequence 0:35:50 Linear regler, standard and LDO 0:37:0 5.7 Pros and Cons 0:41:4 Beispiel Längsregler (Linearregler) 0:49:10 Diskussion Ergebnis 0:52:35 Welligkeit, ripple 0:55:0 5.9 Board space 0:57:44 5.11 PFET as pass device 1:1:40 5.13 Freilaufdiode 1:2:44 5.15 Stabilität 1:5:20 LTSPICE Praktikumsschaltung 1:11:20 Laständerung am Ausgang 1:13:28 Load regulation LoR = 30mV/300mA = 0.1 Ohm 1:15:55 Spannungsverlauf bei Laständerung 1:18:40 Stabilität |
Start
Power
- 5.1 Power Overview
- 5.2 Power Converters
- 5.3 Load Regulation, Line Regulation
Unit 5, 1-21
Begriffe
- Quelleninnenwiderstand
- Statisch
- Line Regulation (LiR):
\( LiR = \frac{\delta V_{out}}{ \delta V_{in}} \) - Power Efficiency (Eta):
\( \eta = \frac{V_{out} \cdot I_{out}}{V_{in} \cdot I_{in}} \)
- Lastausregelung (Load regulation, LoR)
\( LoR = \frac{\delta V_{out}}{ \delta I_{out}} \)
Innenwiderstand
- Dynamisch
- Welligkeit
Ideal power conversion:
Vin · Iin = Vout · Iout
Example: Vin = 2 V, Vout = 4 V, Iout = 100 mA
Calculate Iin.
Iin = 200 mA
Vin · Iin = Vout · Iout
Example: Vin = 2 V, Vout = 4 V, Iout = 100 mA
Calculate Iin.
Iin = 200 mA
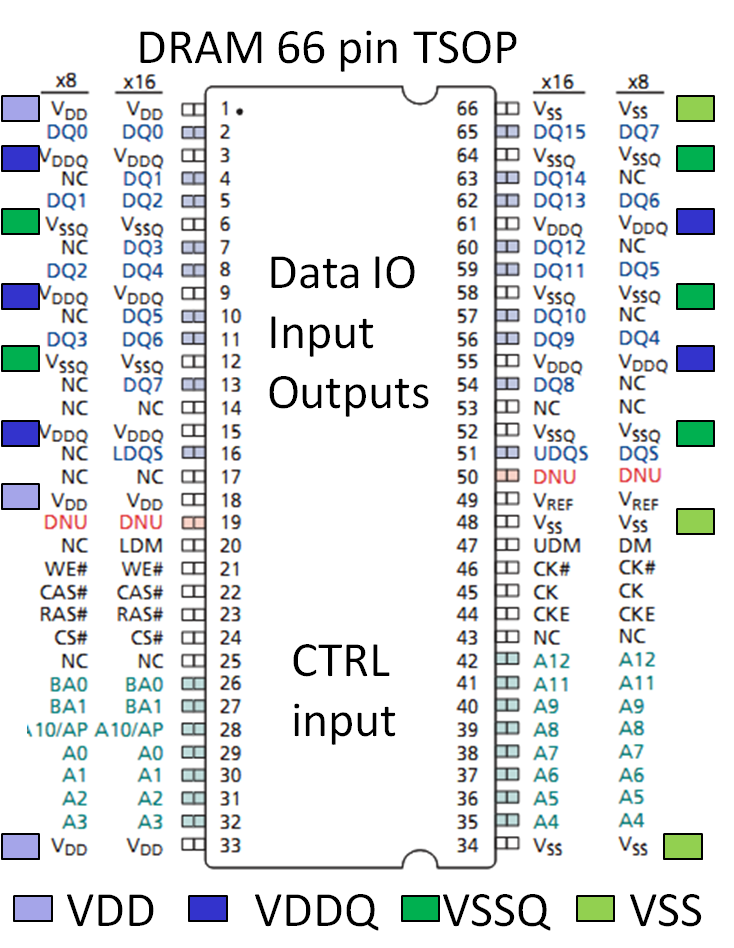
Power grid: DRAM example
- 5.4 DC/DC Power Distribution
|
|
There are separate power supply pins for the data input and outputs (IO).
The number of power pins is proportional to the number of IOs.
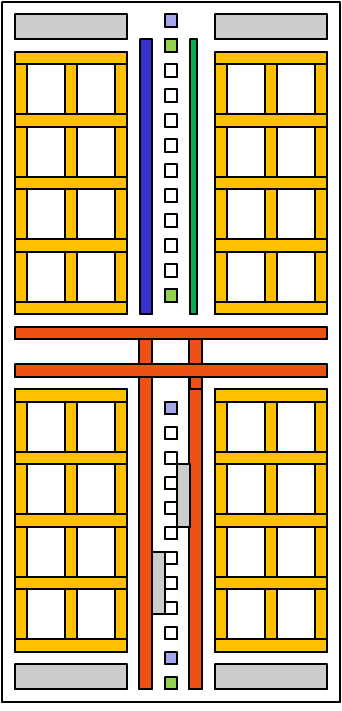
There are separate grids for digital and analog circuits.
Horizontal and vertical lines are connected to a grid and provide power.
The block diagram shows different voltages in different colors in different areas.
Voltage pumps and regulators are shown in grey.
A bandgap reference circuit provides temperature and voltage independent voltages.
The number of power pins is proportional to the number of IOs.
There are separate grids for digital and analog circuits.
Horizontal and vertical lines are connected to a grid and provide power.
The block diagram shows different voltages in different colors in different areas.
Voltage pumps and regulators are shown in grey.
A bandgap reference circuit provides temperature and voltage independent voltages.
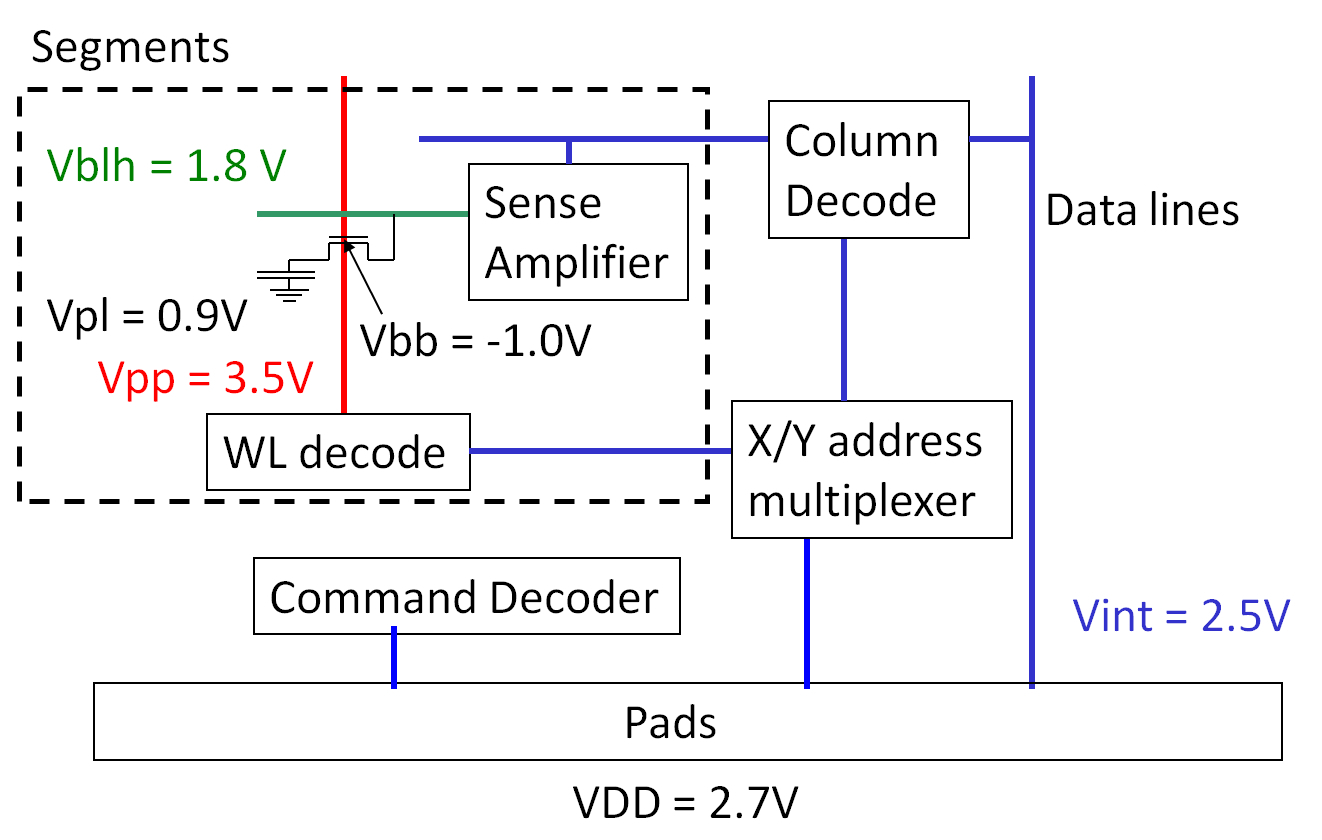
Power on sequence: DRAM
|
A low array voltage is used to save power.
A negative back bias is needed reducing memory cell leakage current.
A high voltage Vpp gives the select transistor overdrive to store the full Vblh level in the memory cell.
Vint is optimized for speed and to be able to drive the IOs.
A high current peak, when power is turned on, has to be avoided.
All capacitances will be charged up at power up.
A negative back bias is needed reducing memory cell leakage current.
A high voltage Vpp gives the select transistor overdrive to store the full Vblh level in the memory cell.
Vint is optimized for speed and to be able to drive the IOs.
A high current peak, when power is turned on, has to be avoided.
All capacitances will be charged up at power up.
Linearregler
- 5.5 Types of Converters
- 5.6 Linear Regulators
- 5.7 Pros and Cons of Linear Regulators
- 5.8 Linear Regulators efficiency and ripple
- 5.9 Linear Regulators board space
Unit 5, 1-21
P3, V3: Linearregler
- 5.10 Linear regulator inside
- 5.11 PFET
Line Regulation (LiR):
I = 100 mA, R = 33 Ω
\( LiR = \frac{\delta V_{out}}{ \delta V_{in}} = \frac{3.26 - 3.18}{ 12 - 6 } = 1.3 \% \)
Power Efficiency (Eta): \( \eta = \frac{V_{out} \cdot I_{out}}{V_{in} \cdot I_{in}} \)
Lastausregelung (Load regulation, LoR)
\( LoR = \frac{\delta V_{out}}{ \delta I_{out}} \)
dI = 100 mA
dVout = 3.257 V - 3.247 V = 10 mV
LoR = 0.1 Ω
R6 zwischen Vx und Vout verhindert Schwingung.
\( LiR = \frac{\delta V_{out}}{ \delta V_{in}} = \frac{3.26 - 3.18}{ 12 - 6 } = 1.3 \% \)
Power Efficiency (Eta): \( \eta = \frac{V_{out} \cdot I_{out}}{V_{in} \cdot I_{in}} \)
Lastausregelung (Load regulation, LoR)
\( LoR = \frac{\delta V_{out}}{ \delta I_{out}} \)
dI = 100 mA
dVout = 3.257 V - 3.247 V = 10 mV
LoR = 0.1 Ω
R6 zwischen Vx und Vout verhindert Schwingung.
Zusammenfassung und nächste Vorlesung
- Typische Versorgungsspannungen in Systemen
- Spannungsversorgungsnetzwerk
- Line Regulation, Load Regulation
- Wirkungsgrad, power efficiency
- Linearregler
- Simulation und Rechnung
Nächstes Mal