Elektronik 322 Analog-Digital-WandlerProf. Dr. Jörg Vollrath21 Digital-Analog-Wandler |

|
Video der 23. Vorlesung 12.1.2022
|
Länge: 1:02:43 |
0:0:45 Digital Analog Wandler R2R 0:3:10 LTSPICE Simulation 0:5:30 Widerstandsänderungen und Fehler 0:10:5 ADC Architekturen 0:12:6 AD Signalkette 0:19:55 Dual Slope Schaltungsanalyse 0:23:2 Simulation 0:26:53 Ein Schalter mit Transistoren 0:31:3 Zeitmessung mit Zähler 0:33:32 Rechnung Dual Slope, Schaltspannungen 0:38:37 Stromgleichung 0:42:17 Vergleich mit LTSPICE 0:44:6 Integrator 0:50:56 Gleichung des ADC 0:55:32 Schnelligkeit, Bandbreite 0:58:32 1 GHz Zähler, 1:1:25 Anzahl Bits und Frequenz 1:4:32 Flash ADC |
Übersicht
- ADC Architekturen
- Dual Slope ADC
- Flash ADC
ADC architectures, resolution and conversion rate
A graph with x axis frequency and y axis resolution shows applications.
Pipeline ADC: 8..16 Bits, 1MHz..4GHz
SAR ADC: 8..18 Bits, 20kHz..8MHz
Sigma Delta ADC: 12..24 Bits, 4Hz..40MHz
Source: QUINTÁNS et al.: METHODOLOGY TO TEACH ADVANCED A/D CONVERTERS, IEEE TRANS. ON EDUCATION, VOL. 53, NO. 3, AUGUST 2010
Investigation of distributer Digikey (01/2017):
Flash ADC (Results: 366): 10 Bit 50 MSps, Range 3..16Bit, 50kHz..26GHz
8 Bit 50kHz AD782 ADI, 3Bit 26GHz HMCAD5831LP9BE ADI, 8 Bit 1GHz MAX104CHC Maxim 16 Bit 166kHz AD7884AQ ADI
Pipeline ADC (Results: 3237): 12 Bit 125MSps, Range 6..16 Bit, 94k..2.6GHz
12 Bit 94kHz MAX1253BEUE+, 12 Bit 2.6GHz ADI, 6 Bit 90MHz MAX1011, 16 Bit 1GHz ADS54 TI
SAR ADC (Results: 8973): 12 Bit 1MSpS, Range 8.. 32Bit 1kSps..500 MSps
32 Bit 1MSps LTC2508 $16, 24 Bit 2MSps LTC2380 $54, 20 Bit 1.6 MSps MX11905 $30 8 Bit 500MSps ISLA118P5 Intersil $50, 8 Bit 3MSps MAX 11116 $2
Sigma Delta ADC(Results: 1928): 24 Bit 256kSps Range: 8..32 Bit , 3Sps..3.2GSps
16 Bit 3.2GSps(100MHz) AD6676 ADI $200, 16 Bit 160MSps(2.5MHz) AD9262 ADI $48, 12 Bit 3.3kSps ADS1015 TI $2, 32Bit 1MSps LTC2508 $17
Dual Slope (Results: 28): 15 Bit 30Sps
Pipeline ADC: 8..16 Bits, 1MHz..4GHz
SAR ADC: 8..18 Bits, 20kHz..8MHz
Sigma Delta ADC: 12..24 Bits, 4Hz..40MHz
Source: QUINTÁNS et al.: METHODOLOGY TO TEACH ADVANCED A/D CONVERTERS, IEEE TRANS. ON EDUCATION, VOL. 53, NO. 3, AUGUST 2010
Investigation of distributer Digikey (01/2017):
Flash ADC (Results: 366): 10 Bit 50 MSps, Range 3..16Bit, 50kHz..26GHz
8 Bit 50kHz AD782 ADI, 3Bit 26GHz HMCAD5831LP9BE ADI, 8 Bit 1GHz MAX104CHC Maxim 16 Bit 166kHz AD7884AQ ADI
Pipeline ADC (Results: 3237): 12 Bit 125MSps, Range 6..16 Bit, 94k..2.6GHz
12 Bit 94kHz MAX1253BEUE+, 12 Bit 2.6GHz ADI, 6 Bit 90MHz MAX1011, 16 Bit 1GHz ADS54 TI
SAR ADC (Results: 8973): 12 Bit 1MSpS, Range 8.. 32Bit 1kSps..500 MSps
32 Bit 1MSps LTC2508 $16, 24 Bit 2MSps LTC2380 $54, 20 Bit 1.6 MSps MX11905 $30 8 Bit 500MSps ISLA118P5 Intersil $50, 8 Bit 3MSps MAX 11116 $2
Sigma Delta ADC(Results: 1928): 24 Bit 256kSps Range: 8..32 Bit , 3Sps..3.2GSps
16 Bit 3.2GSps(100MHz) AD6676 ADI $200, 16 Bit 160MSps(2.5MHz) AD9262 ADI $48, 12 Bit 3.3kSps ADS1015 TI $2, 32Bit 1MSps LTC2508 $17
Dual Slope (Results: 28): 15 Bit 30Sps
AD conversion signal chain
Analog signal|
Preamplifier (range adjustment, impedance matching) Anti-alising filter Sampling Quantization Digital coding (error correction, filter) |
 |
Zählverfahren, Dual-Slope-Verfahren
|
\( C = \frac{Q}{U} = \frac{I dt}{dU} = \frac{\frac{U_{in}}{R} dt}{dU} \)
\( t_1 = \frac{C dU R}{U_{in}} \)
\( t_2 = \frac{C dU R}{U_{ref}} \)
\( \frac{t_2}{t_1} = \frac{U_{in}}{U_{ref}} \)
\( U_{in} = \frac{t_2}{t_1} U_{ref} \)
Eine Kapazität C im Integrator wird abwechselnd mit Vin geladen und mit Vref entladen.
Je nach Höhe der Spannung Vin ändert sich die Zeitdauer für einen Lade- Entladevorgang.
Ein Zähler kann diese Zeit messen.
Dieses Verfahren wird bei Multimetern verwendet.
Wie gross ist der Eingangsspannungsbereich?
| Vin in V | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| t1 in ms | 3.85953 | 4.23152 | 4.76959 | 5.61642 | 7.14093 | 10.7025 |
Flash ADC
OperationResolution BSpeedPower | cmosedu_models.txt |
The Flash ADC generates a thermometer code.
For each level one comparator is needed. High count of comparators, high input capacitance.
High resolution requires low comparator offset and high gain to generate a full level digital signal.
The offset of a comparator depends on the size of the CMOS input transistors:
Voffset ∝ \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{W \cdot L}} \)
Lower noise means higher area and higher input capacitance.
If the requirement for comparator offset is not met or noise is present sparkle codes can happen.
The thermometer code is corrupted having more than one transition from 0 to 1.
The code for the first '01' transition is 'OR'ed with the code of the second '01' transition.
Additional digital circuit can be required.
Comparators can feedback noise to the reference voltage ladder. Capacitive coupling between comparator output and intput.
| Thermometer code | Binary Code | ||||||||
| T6 | T5 | T4 | T3 | T2 | T1 | T0 | B2 | B1 | B0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
For each level one comparator is needed. High count of comparators, high input capacitance.
High resolution requires low comparator offset and high gain to generate a full level digital signal.
| Number of Bits | Maximum Offset | Gain |
| 4 | 0.0625 · Vref | 16 |
| 8 | 0.004 · Vref | 256 |
| 10 | 0.001 · Vref | 1024 |
| 12 | 0.0025 · Vref | 4048 |
The offset of a comparator depends on the size of the CMOS input transistors:
Voffset ∝ \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{W \cdot L}} \)
Lower noise means higher area and higher input capacitance.
If the requirement for comparator offset is not met or noise is present sparkle codes can happen.
The thermometer code is corrupted having more than one transition from 0 to 1.
| Correct code: | 000000011111111 | Encoded binary code | 1000 |
| Sparkle code: | 000000010111111 | Encoded binary code | 1110 |
Additional digital circuit can be required.
Comparators can feedback noise to the reference voltage ladder. Capacitive coupling between comparator output and intput.
SAR ADC: Blocks
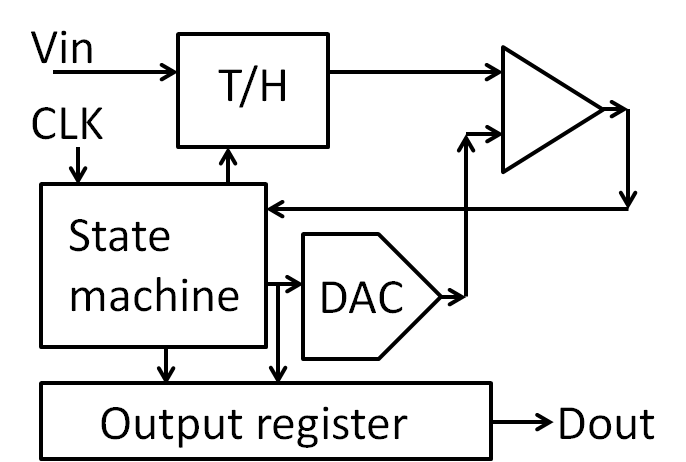 |
At the beginning of the conversion an input signal is sampled.
The comparator compares it with the output of the DAC.
The state machine sets the MSB depending on the outcome of the comparison and then tries the next bit.
The comparator compares it with the output of the DAC.
The state machine sets the MSB depending on the outcome of the comparison and then tries the next bit.
SAR ADC: Flow, Algorithm, Simulation
|
Vref = 1V Vin = 0.6 V Stellen Sie den zeitlichen Verlauf der internen Vergleichsspannung Vout des SAR ADC dar. |
Input: 0.6
1 * 0.5 + 0 * 0.25 + 0 * 0.125 + 1 * 0.0625 + 1 * 0.03125 + 0 * 0.015625 + 0 * 0.0078125 + 1 * 0.00390625
0.59765625
SAR ADC: Flow, Algorithm, Simulation
|
Set MSB to 1: 100000 Loop until LSB set: Compare DAC output with analog input: If DAC output > analog input reset current bit. Try and set next bit. End Loop Blue line shows analog input voltage. Green shows output of internal DAC. Red shows output code with MSB first. |
1 * 0.5 + 0 * 0.25 + 0 * 0.125 + 1 * 0.0625 + 1 * 0.03125 + 0 * 0.015625 + 0 * 0.0078125 + 1 * 0.00390625
0.59765625
SAR ADC: Benefits and Challenges
- Separate blocks can be optimized individually
- Comparator gain and offset:
LSB * gain = Vref
Voffset < LSB
ΔV << LSB: Metastability - Conversion time: n-bits * Settling time
tconv= n * tsettle
Mittelwertbildung
Mittelwertbildung Formel: y[i] = (x[2 * i] + x[2 * i +1]) / 2|
Der Wertebereich verdoppelt sich. Das Signal-Rausch Verhältnis ändert sich, da nur noch halb so viele FFT Frequenzen zur Verfügung stehen. \( 20 log \left( \sqrt{2} \right) = 10 log \left( 2 \right) = 3 dB \) Das letzte Bit hat einen Rauschanteil. |
Man kann auch von einer Oversamplingrate OSR von 2 sprechen.
Der Signal-Rausch-Abstand erhöht sich bei Mittelwertbildung mit OSR Werten um:
\( 10 log \left( OSR \right) \)
Die Grafik zeigt ein Sinussignal mit einer Amplitude von Ua = 128 und einer Auflösung von 8 Bit und eine Mittelwertbildung.
Der Effektivwert ergibt sich bei einer Sinusspannung mit dem Faktor \( \sqrt{2} \).
\( A_{signal} = 20 \cdot log_{10}(\frac{Ua}{\sqrt{2}}) \)
\( A_{signal} = 20 \cdot log_{10}(\frac{128}{\sqrt{2}}) = 39 dB \)
Man erwartet ein SQNR = 6.02 * 8 dB + 1.76 dB = 49.78 dB
Das wäre ein Rauschpegel von - 10.78 dB (Grüne Linie).
Dieses Rauschen wird auf alle dargestellten Frequenzen (128 = 256 / 2 = NFFT / 2 ) aufgeteilt.
\( v_{Ges} = \sqrt{N \cdot v_i^2 } \)
\( dA_{NFFT} = 20 \cdot log_{10} \left(\sqrt{\frac{NFFT}{2}}\right) = 10 \cdot log_{10}\left(\frac{NFFT}{2}\right) = 21 dB \)
Das Rauschen der einzelnen Frequenzen liegt dann in etwa bei -31 dB (Rote Kurve).
Bei der logarithmischen Darstellung der Frequenz liegen die Punkte der höheren Frequenzen dichter zusammen. In der Darstellung sieht man eine starke Schwankung der einzelnen Werte.
Eine Ablesung des Signal-Rausch Verhältnisses aus der Graphik ist deshalb nicht sinnvoll.
Der Signal-Rausch Abstand muss numerisch berechnet werden.
Oversampling ADC: History
Nyquist ADCOversamplingfCLK = OSR · 2 · fbw Clock frequency is much higher than bandwidth. Pulse count Modulation (PCM)Predictive CodingQuantize difference of the signal Sigma delta converter |
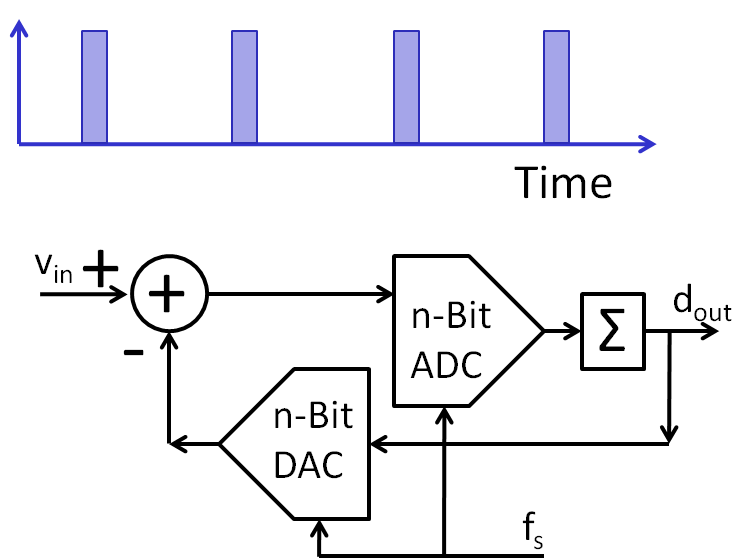 |
Sigma Delta ADC Architectures
 |
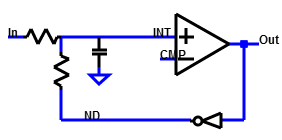   |
First order passive Sigma Delta Modulator
Internal voltage levels:The voltage V(INT n+1) at clock cycle n+1 is:\( V_{int n+1} = V_{int n} + \frac{\delta t}{C} \left( \frac{ V_{not(Dout)} - V_{int n}}{R} + \frac{V_{in} - V_{int n}}{R} \right) \) \( V_{int n+1} = V_{int n} + \frac{\delta t}{C \cdot R} \left( V_{not(Dout)} + V_{in} - 2 \cdot V_{int n} \right) \) \( \delta t \) is the period of the clock. \( V_{Dout} \) in a real logic circuit is 0V or VDD. These equations are used for a high level simulation. High level simulation: 1st order sigma delta simulation Since Vint has to stay between 0V and VDD: \( \frac{\delta t}{C \cdot R} 2 V_{DD} \lt V_{DD} \) \( C \cdot R \gt \frac{2}{f_{sample} } \) \( \frac{1}{C \cdot R} \lt \frac{f_{sample} }{2} \) The bandwidth limit of RC has to be smaller than fsample/2. The bandwidth limit of RC has to be greater than the interested bandwith. fsample/2/OSR \( 2 \pi f_{bw} \lt \frac{1}{C \cdot R} \lt \frac{f_{sample} }{2} \) |
On the left the difference of V(in) and V(D) is integrated and then
compared with V(CMP). The comparator operates with the clock frequency and
gives for each clock cycle a new value.
A simple passive first order sigma delta converter uses resistors and capacitances.
This circuit is according to Baker, "CMOS integrated cicuits", Figure 6.4
A simple passive first order sigma delta converter uses resistors and capacitances.
This circuit is according to Baker, "CMOS integrated cicuits", Figure 6.4
Schalter und Sample and Hold
|
Vergleich der Wandlerprinzipien
Dual-slope Verfahren
Flash ADC
SAR ADC
Sigma Delta ADC
Zusammenfassung und nächste Vorlesung
- Übersicht
- Dual Slope
- Flash
- SAR
- Sigma Delta Wandler
Nächstes Mal