- Projektpraktikum Elektronik
SoSe 2026 Projektpraktikum: Elektroniklabor
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jörg Vollrath
Motivation
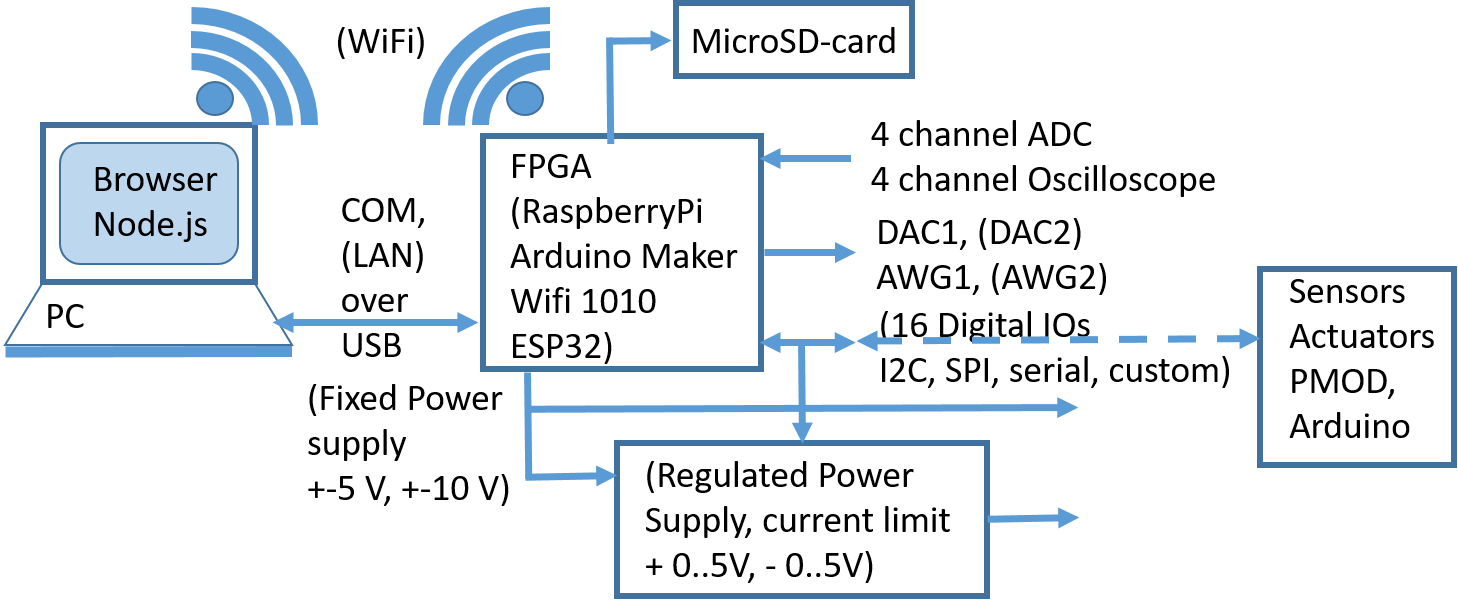
Ein Elektroniklabor benötigt Spannungsversorgung, Funktionsgenerator, Spannungsmesser, Oszilloskop und digitale IOs, um Schaltungen zu untersuchen und zu entwerfen.
Auf dem Markt gibt es kompakte Geräte (ADALM2000, Analog Discovery, Red Pitaya, Moku Go) die einige dieser Funktionen vereinigen.
Eine ideale preisgünstige Variante mit allen Funktionen, 4 Kanal Oszilloskop, minimaler Software Installation und schönem Userinterface ist nicht erhältlich.
Dieses Praktikum beschäftigt sich damit eine vorhandene preisgünstige Open Source Realisierung weiter voran zu treiben.
Dies ist ein Projektpraktikum mit 3 SWS begleitet von 1 SWS Projektmanagment.
Es werden Gruppen zu jeweils 4 (3) Studierenden gebildet.
Ein Block mit 180 min stehen mit Betreuung pro Woche zur Verfügung.
Am Ende wird eine Präsentation und ein Bericht bewertet.
Status
The current status of hardware and software is shown first:
Research Summary
Installation Instructions
The project is available at github JVollrath NodeEEBench.
The current version can be download as zip file NodeEEBenchV20261302.zip.
Unpack the files into "C:\temp". All files should then be in the directory "C:\temp\NodeEEBench".
The subdirectories "node" and "node_modules" contain the node executable to provide a web server and connection to a serial interface.
Hardware: BASYS3
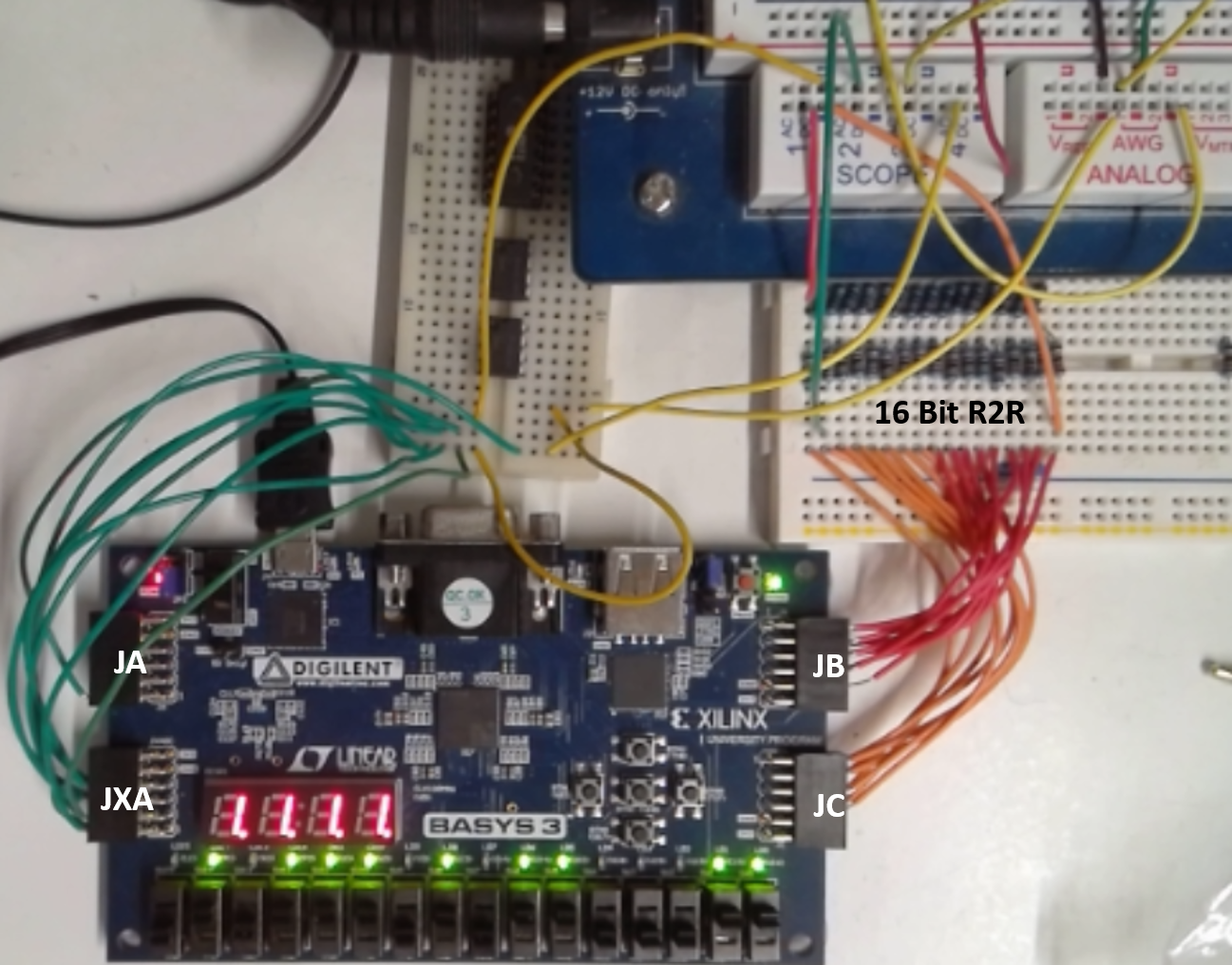
Figure: BASYS3 FPGA Board with R2R DAC and Electronic Explorer
Hardware features:
4 channel, 12-Bit, 125 kSps, 0..1 V range ADC oscilloscope FPGA (XADC)
1 channel, 16-Bit, 30kSps, 0..3.3 V range, 15us settling time, 100k,220k R2R DAC
4k samples transfered via UART with Baud rate 230400
Pins Oscilloscope: OSC1 JXA 1 in, 7 GND; OSC2 JXA 2 in, 8 GND; OSC3 JXA 3 in, 9 GND; OSC4 JXA 4 in, 10 GND;
Pins AWG: JC upper 8 Bit 10,9,8,7,4,3,2,1; JB lower 8 Bit 10,9,8,7,4,3,2,1;
16 Bit R2R DAC: left side output D15 connected to scope 1, right side D0 and GND connection.
The FPGA configuration is done using the VHDL project files in the directory C:\temp\NodeEEBench\Xilinx\EEBench.
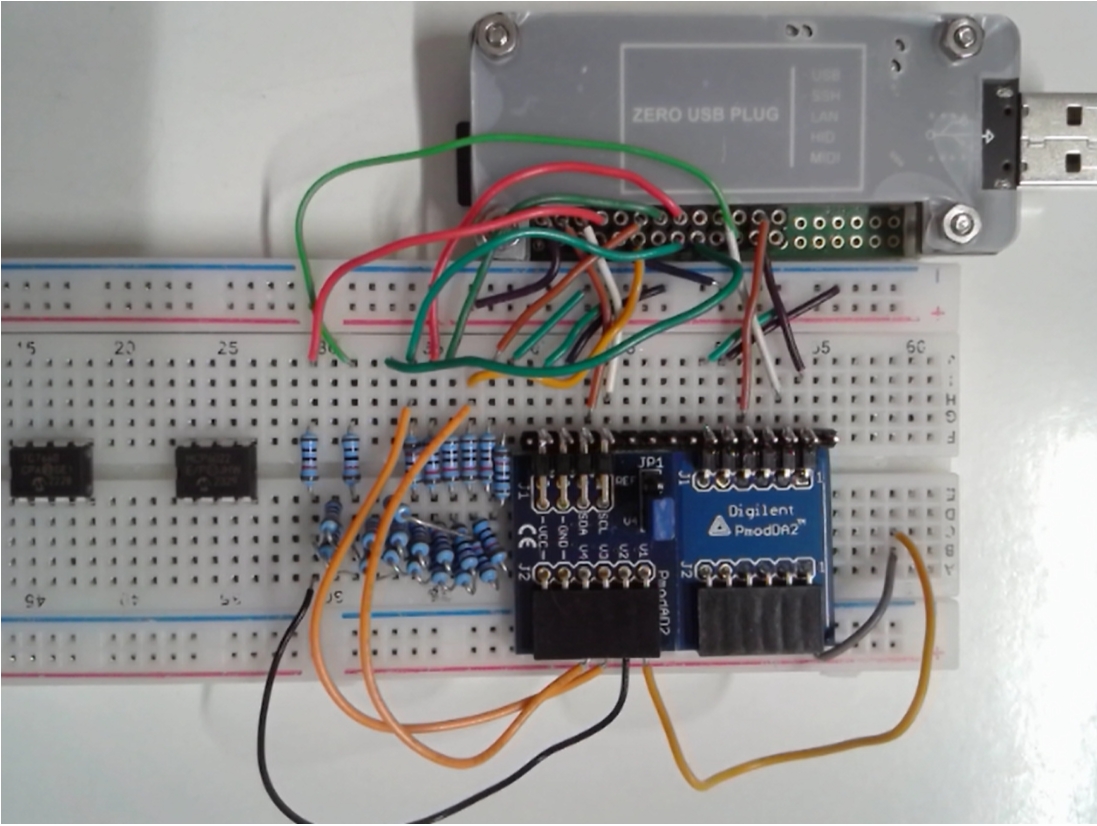
Hardware: Arduino
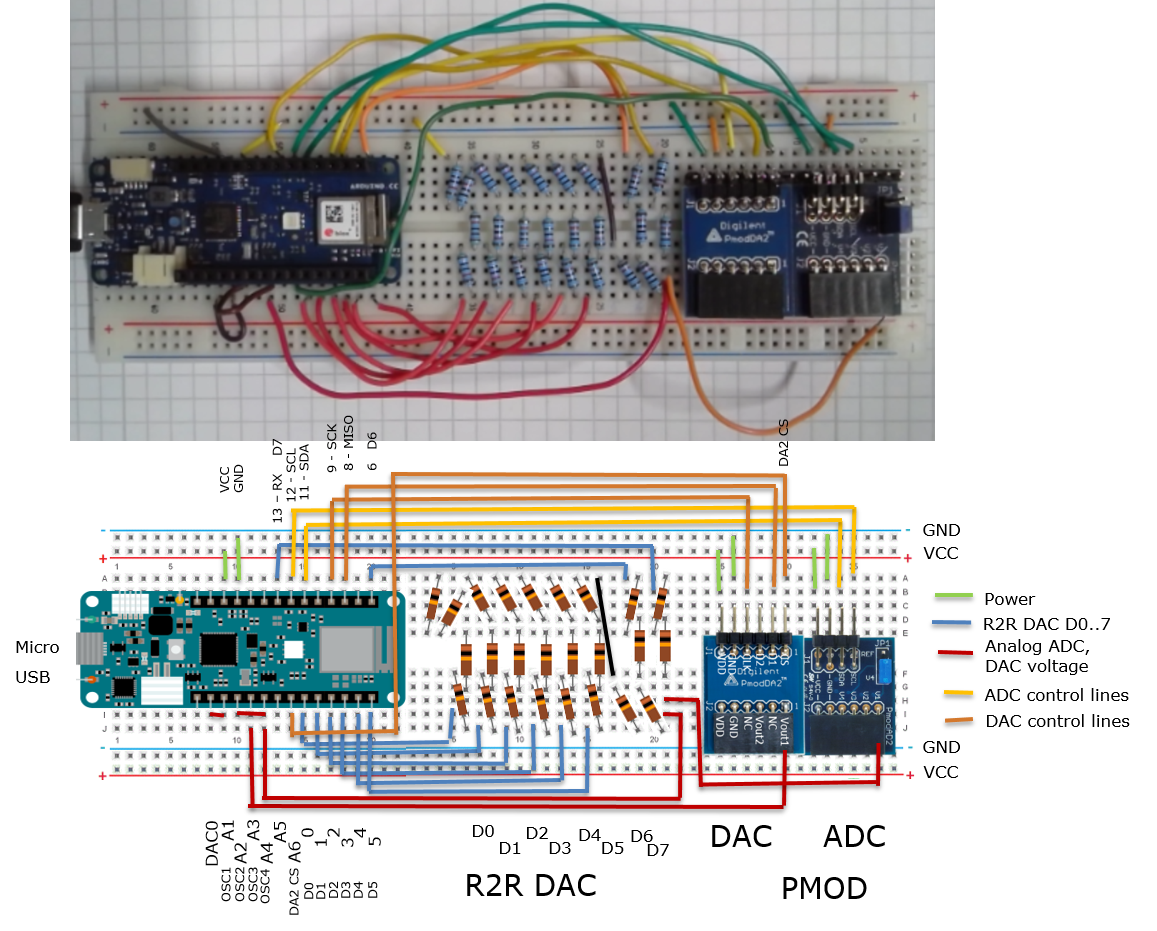
Additional ADC and DAC are realized with Digilent PMOD AD2, Digilent PMOD DA2, R2R DAC with 10k,20k resistors.
In the subdirectory Arduino are different sketches:
- "EEBench" the default configuration for NodeEEBench.bat.
- "DataConverterCharV4" realizes an R2R DAC for data converter investigation StartServerAx.bat.
Detailed description is available at Interface Electronics ADC DAC Analysis Laboratory - "DataConverterCharV5" realizes an serial C DAC for data converter investigation StartServerAx.bat.
Low cost serial DAC simulation, realization, error correction and characterization - "DataConverterCharSerialSAR" realizes a serial SAR circuit.
Software: User interface
Start the program with "C:\temp\NodeEEBench\NodeEEBench.bat".
A command window is started, the serial communication with a BASYS3 or Arduino board established and a web browser connects to "localhost:3000" to display the graphical user interface.
Besides the standard interface started with "C:\temp\NodeEEBench\NodeEEBench.bat" There is an additional special Arduino Interface for INL, DNL and SNR, FFT operation, which can be started with "C:\temp\NodeEEBench\StartServerAx.bat"
Detailed description is available at Interface Electronics ADC DAC Analysis Laboratory
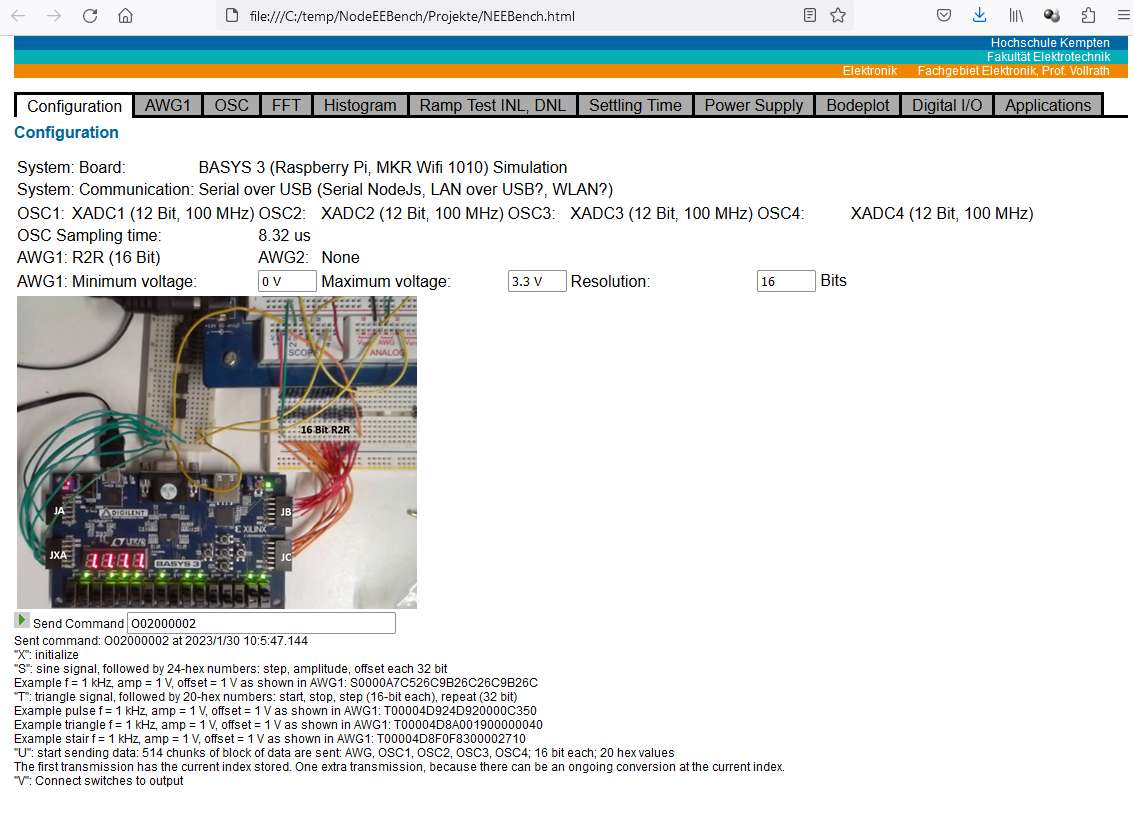
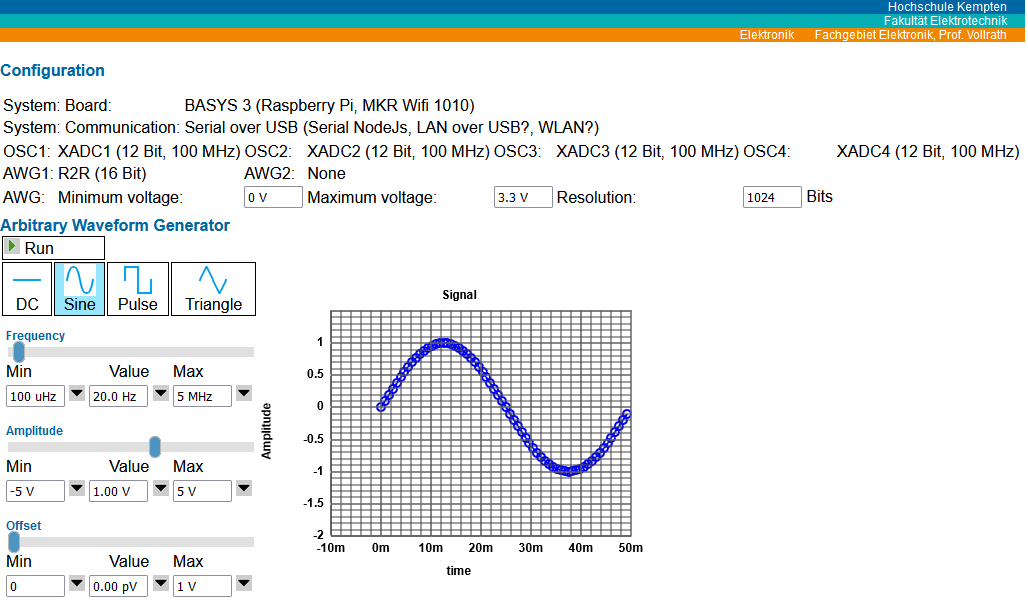
Figure: Configuration and signal generator user interface
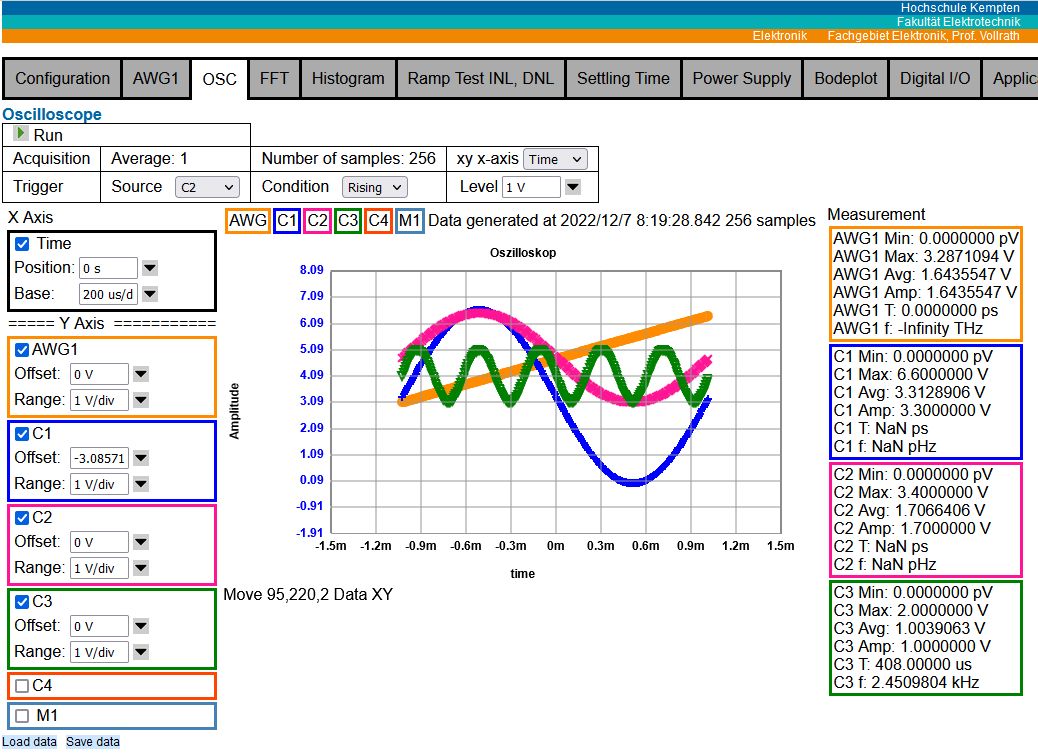
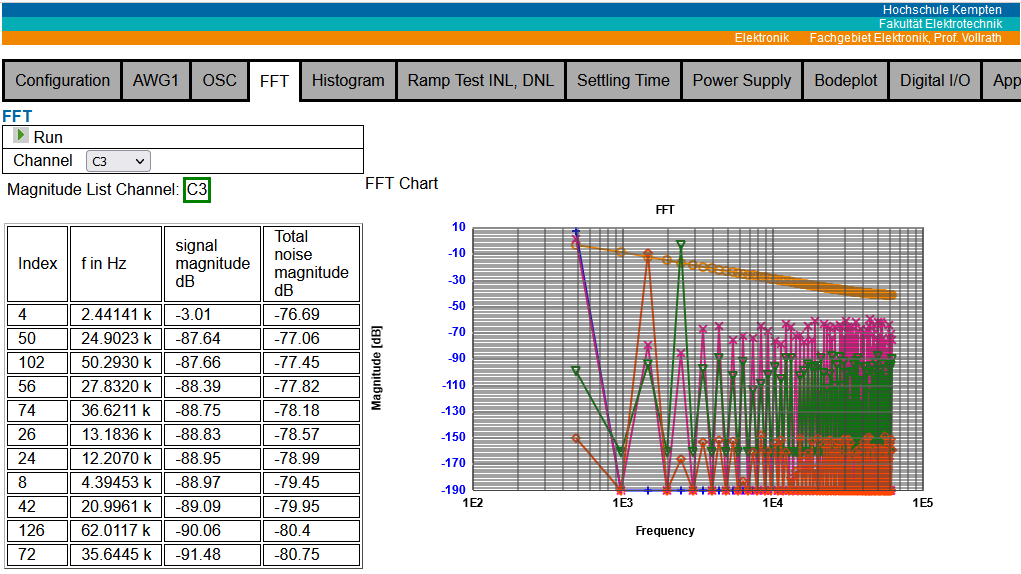
Figure: Oscilloscope and FFT interface V05
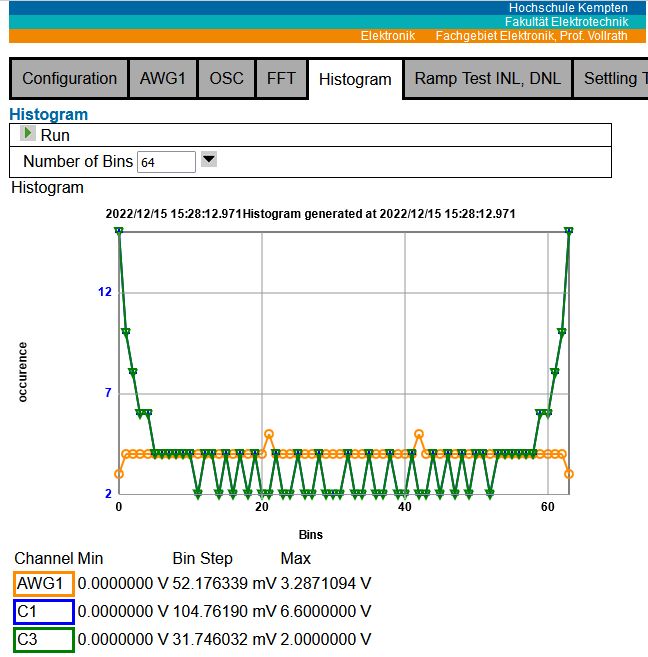
Figure: Histogram interface V06
Software features
Configuration with individual serial command transfer.
AWG: DC, stair, triangle and sine generator with frequency, amplitude and offset
OSC: 4 channel and AWG with 8..4096 sample selection, xy display, voltage and code selection, rising, falling single channel trigger, minimum, maximum, average, amplitude, period and frequency calculation.
There is voltage sample data and code data display available. A measured signal can be directly compared to the golden AWG signal in voltage or code.
FFT: AWG1, OSC1, OSC2, OSC3, OSC4 with highest magnitude frequencies and total noise magnitude for ENOB, SINAD, SFDR, SDR calculation.
Histogram with adjustable (16..256) number of bins.
Ramp Test INL, DNL
Lookup Table
Unique features (Work in progress)
Signalgenerator DAC and Oscilloscope ADC integer value display.
Lookup table application for arbitrary waveform generator.
Oscilloscope data processing and feeding output to arbitrary waveform generator.
Serial interface data processing.
ADC, DAC, INL, DNL analysis.
Vorgehen 2026
- Sichten und Inbetriebnahme des vorhandenen Materials.
- Transfer auf CMOD A7
- PMOD DA2, PMOD AD2, MCP4728 DAC, I2C/SPI Digital Interface Page, SRAM Memory Buffer
- Präsentation der Ergebnisse
- Projektbericht
Planen Sie ihre Aktivitäten und überprüfen Sie ihren Projektfortschritt.
Sichern Sie Teilergebnisse durch geeignete Versionierung.
Projekt Ideen
- Umsetzung mit A7 CMOD FPGA
- Systematische Beschreibung von Test und Inbetriebsnahme
- Inbetriebnahme anderer Mikroprozessoren
RaspberryPi Zero, Infineon uP, TI uP, STMicro uP - Unterstützung weiterer Datenwandler: ADC, DAC
- Implementierung einer Spannungsversorgung
- Implementierung digitaler IOs und Busse (I2C, SPI, UART)
- Implementierung von Steuerung und Regelung
- Software
Test, Dokumentation, Modularisierung, Open Source, Github, Versions - Anwendungsfälle
Bauelementemessung, Datenwandler, Motorsteuerung, Ladungspumpe, Operationsverstärker, Sample and Hold, Duty Cycle Regler für Buck Converter, Schaltungen, Graphical Interface um SAR Steuerung zu implementieren - Features
Tracking, Priorisierung, Test, Hardware/Software matching - Second waveform generator AWG2
Bauteile
- A7 CMOD
- BASYS3 FPGA
- Arduino MKR WIFI 1010
- Raspberry Pi Zero W
- (Infineon, STMicro, TI MSP3240 Mikroprocessor board)
- Datenwandler PMODs: Digilent DA1, DA2, AD1, AD2; MAX
- Power supply
List?? Analog devices Eval, TI Eval board - Schaltungsbauteile
- Power ICs
Bauteile
BASYS3 Board

Arduino MKR WIFI 1010

RaspberryPi Zero W2
A7 CMOD
TI MSP3240
ST Micro Nucleo
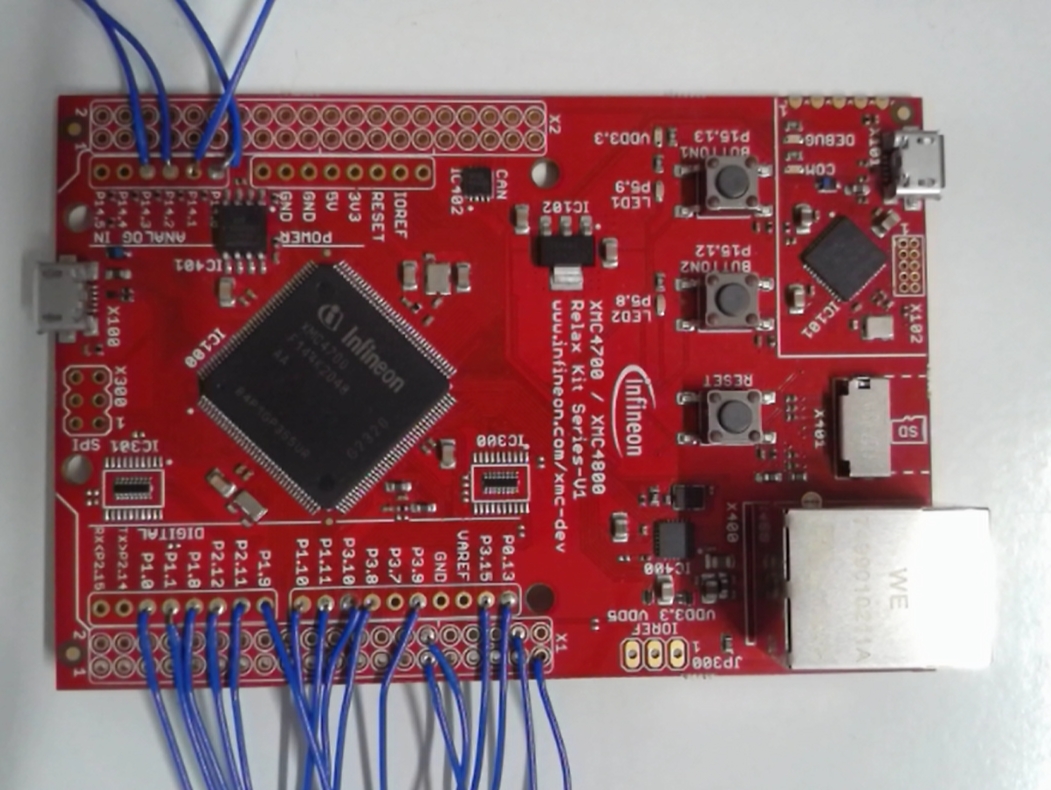
Infineon XMC4700 Relax
PMOD ADC, DAC

Digilent
LM27762EVM
Geräte
Breadboard, Electronic Explorer, Multimeter, Seitenschneider, KomponentenabbiegevorrichtungBreadboard
Electronic Explorer
Multimeter

Seitenschneider

Abisolierer

ADALM2000

Red Pitaya
Summary 2025
| Rank | Topic | Link |
| 1 | Raspberry Pi Zero W | |
| 1.1 | Raspberry Pi Zero W OS Installation | |
| 1.2 | Raspberry Pi Zero W Node Installation | |
| 1.3 | Raspberry Pi Zero W Python Installation | |
| 1.4 | Raspberry Pi Zero W Webserver Installation | |
| 5 | Improve server startup (path, autostart RaspberryPi) | |
| 2 | Hardware detection with server | |
| 3 | Digital IO implementation (Arduino) | |
| 4 | Server side virtual hardware (Simulation) | |
| Python AWG and Oscilloscope | ||
| Node Red functionality implementation using graphical programming | ||
| VP+, VP-, DC positive and negative generator |
Lessons learned 2025
- Motivation at start of project needed
- Longer introduction of system needed
Modularity, Hardware, Server, HTML code, Javascript functionality, communication, files and folders, hardware, software distribution and interfaces, detailed feature list - Guideline for presentation should improve format
- Regular general progress and issue tracking
- No understanding of serial communication and server client communication.
Some features were doubled up. - Improve documentation: Table Picture, List/Tree, Link to detail use colors, variables, sections, HTML, JavaScript
- New Goal: Raspberry Pi receives serial commands via USB for ADC, DAC control like (Arduino/FPGA)
- New Goal: Server log via Internetpage
- New Goal: Why no Python implementation of webserver with current web pages and websocket?
- New Goal: Test flow generator and run for regression testing
Server Side Hardware Sine Generator Simulation 2025
Specific Implementation and Test
- Server is started 'NodeEEBench.bat' and detects no serial attached hardware
Implementation in ServerEEBench.js: var devMan ="Simulation"; - Simulation receives commands
Implementation in ServerEEBench.js:
if (serialPort) { serialPort.write(cmdName); // hex(cmdName) } else { // Simulation simX(cmdName); .. // implement send data } - Simulator: O Command (ServerEEBench.js)
function simX()
Variables: blockSize, mulTime - Simulator: S Command (ServerEEBench.js)
function genSine()
Verification: Select OSC Time Base and Block size, Select AWG Sine 10Hz, 100Hz, 1.5 kHz, Run OSC
Voltage scaling verified.
Missing frequency verification of interaction of step with TimeBase
NEEBench.html: BASYS3 10ns DAC (fcalc), 8320ns ADC, OSC sampling rate(O command), block size (dataMax)
function genCmdAWG():fcalc = 1E8; dataMax = 512; // 512, 1024, 2048 selected at OSC tab nSample = 13 * 128; // 1664 = 8.32us / 10 ns * 2 FPGA = Math.trunc(8.32E-6/10E-9*2) var timeX = (timeBase + 1)/4; // For slow timeBase sampling gets slower var nCycle = Math.round(dataMax / fCalc * timeX * nSample * frequency); // number of cycles if ((nCycle % 2) == 0) { nCycle = nCycle + 1; } // make odd frequency = nearestPrime(nCycle) * fCalc / dataMax / timeX / nSample; // prime corrected frequency step = Math.trunc(1024 * 1024 * 8 / fCalc * nSample * frequency);Acquisition time: tA = 1/fcalc * nSample * (timeBase+1) * dataMax;
Number of cycles nCycle = tA/tf = tA * frequency
step = 1024 * 1024 * 8 * nCycle / dataMax / timeX
step should be divided by 8 * 1024 * 1024
Not working yet?! - Simulator: U Command (ServerEEBench.js)
Integer values into string dataBufX (simX), set dataReady and emit to client (socket.on('cmd',..))
if (serialPort) { serialPort.write(cmdName); // hex(cmdName) } else { // Simulation simX(cmdName); // console.log("Simulation: " + dataReady); if (dataReady == 1) { // send data // emit string console.log(dataBufX.length/22 + "," + dataBufX.length + "," + dataBufX.substring(0,50)); // dataBufX socket.emit('newData',{value: dataBufX}); dataReady = 0; } } - Eliminate use of fs in ServerEEBench.js
- Use lower case USB manufacturer id in ServerEEBench.js for linux compatibility
Bugs:
Missing initialization of hardware with a full set of commands at start of server
Missing features:
- emit found hardware device to client and client updates status
- Implement webserver and websocket in Python
Test 2025
Laboratory PC: NodeJs server on PC, USB connection to Arduino or BASYS 3
(Laboratory PC shares Network connection with PI:
USB to RaspberryPi Gadget Mode with NodeJs server; Raspberry PI USB connection to Arduino or BASYS 3)
USB to RaspberryPi Gadget Mode with NodeJs server and PMOD DA2, AD2 control
Dual WIFI access point connected via LAN to PC and WIFI to RaspberryPi
Laptop Wifi connection to RaspberryPi Access point and USB connection to Arduino or BASYS 3
Hardware: (Laptop, Node), (Laptop, Node, BASYS3), (Laptop, Node, Arduino), (Laptop, Node, RaspberryPi Zero W Sim), (Laptop, Node, RaspberryPi Zero W, Arduino), (Laptop, Node, RaspberryPi Zero W, BASYS3), (Laptop, Node, RaspberryPi Zero W, PMOD ADC, PMOD DAC)
(Start Server: NodeEEBench.bat)
Select Configuration
Select OSC: Number of samples (8, 256, 512, 4096) and Time Base (Table Hardware and available Timebase)
Check console log of server for correct data transfer
Select AWG: Waveform Sine, frequency, offset 0.5 V, amplitude 0.5 V
Select OSC: Run and check result amplitude, average, frequency
Check OSC Trigger, Unit, xy axis
Select FFT: Run, check power spectrum
Select AWG: Waveform (DC, Pulse, Triangle, Stair) frequency, offset 0.5 V, amplitude 0.5 V
Table: Hardware and available operating range
| Hardware | AWG output voltage range | AWG fmin | AWG fmax | OSC input voltage range | Time base min | Time base max |
BASYS3 Boad, Arduino Wifi Maker 1010, serial at PC, Laptop
| AWG sine frequency | Calculated frequency | OSC sampling | timeBase O command | Block Size | Platform |
| 1 Hz | 200 ms/div | 10 | 256 | Simulator, FPGA, Arduino, Raspberry Pi Zero W 2 | |
| 100 Hz | 5 ms/div | 1 | 256 | Simulator, FPGA, Arduino, Raspberry Pi Zero W 2 | |
| 1 kHz | 200 us | 1 | 256 | Simulator, FPGA, Arduino, Raspberry Pi Zero W 2 | |
| 10 kHz | 200 us | 1 | 256 | Simulator, FPGA, Raspberry Pi Zero W 2 | |
| 100 kHz | 50 us | 1 | 256 | Simulator, FPGA | |
| 1 MHz | 5 us | 1 | 256 | Simulator | |
| 10 MHz | 20 ns | 1 | 256 | Simulator | |
| 100 MHz | 20 ns | 1 | 256 | Simulator |
Weiterentwicklung 2025
The frequency of a selected sine waveform for the Arduino platform is not calculated correctly.
Timing calculations and measurements should be done.
2 waveform generators should be implemented.
PMOD AD2 (I2C) and PMOD DA2 (SPI) should be enabled.
Timing of communication between Arduino and PMOD is measured.
24 cycles 1 us/1 MHz are used for each DA channel.
48 cycles can be used for 2 channels.
This should give a sample rate of 20 kHz.
30 MHz macimum clock cycle should be possible giving 600 kHz, but 8 us settling time.
(1) DA Investigation 2 channels FPGA
(2) ADC Investigation 4 channels FPGA