Microelectronics13 Faults and Test in MicroelectronicsProf. Dr. Jörg Vollrath12 Power, Clock, IO |
Video of lecture 13 (26.05.2020)
|
Länge: 1:01:57 |
0:0:0 Layout NCC checking transistor sizes 0:0:35 Silicon compiler layout result 0:3:48 Laboratory layout 0:6:31 M2 line 0:10:15 Silicon compiler result 0:13:44 Number of metal layers of a logic chip 0:16:10 Area of design styles 0:21:10 Design for test 0:23:13 Yield 0:28:16 Test 0:33:25 Test a truth table 0:34:43 Faults: Stuck at, bridging, transition 0:37:10 Layout and defects 0:43:10 Model of fault and defect sizes 0:45:0 Wafer maps 0:47:21 Defects and faults, fault coverage 0:52:41 Modeling defects: R and C# 0:54:13 Classical fault model 0:56:53 Timing delay fault 0:58:18 Process variations 1:0:35 Guard band 1:1:45 Memory test flow 1:5:37 Memory tester and handler |
Overview
Review:- Power calculation
- Clock
- Pads
Today Test:
- Yield and faults
- Defect oriented testing
Memory tester and component handler
 |

|
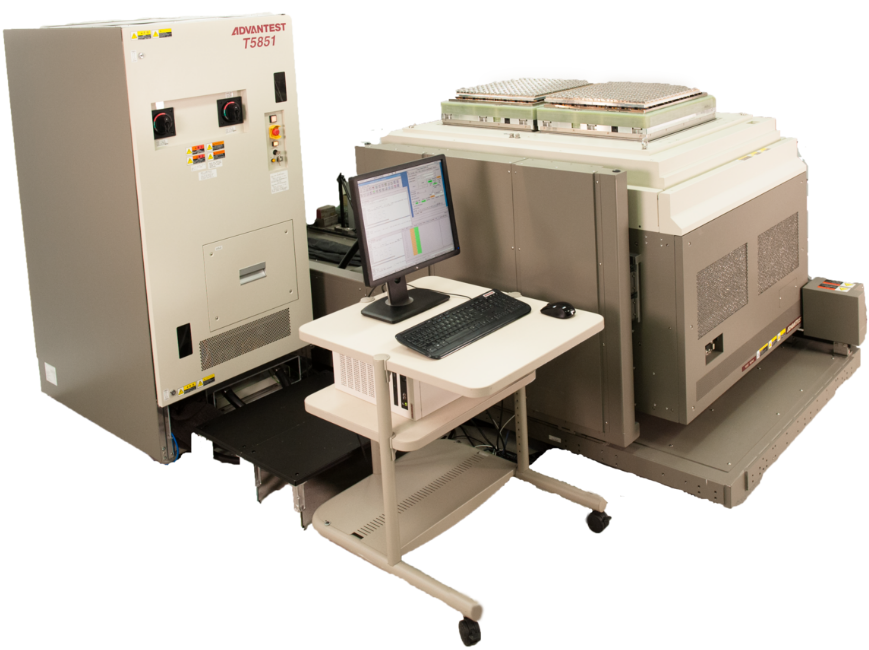
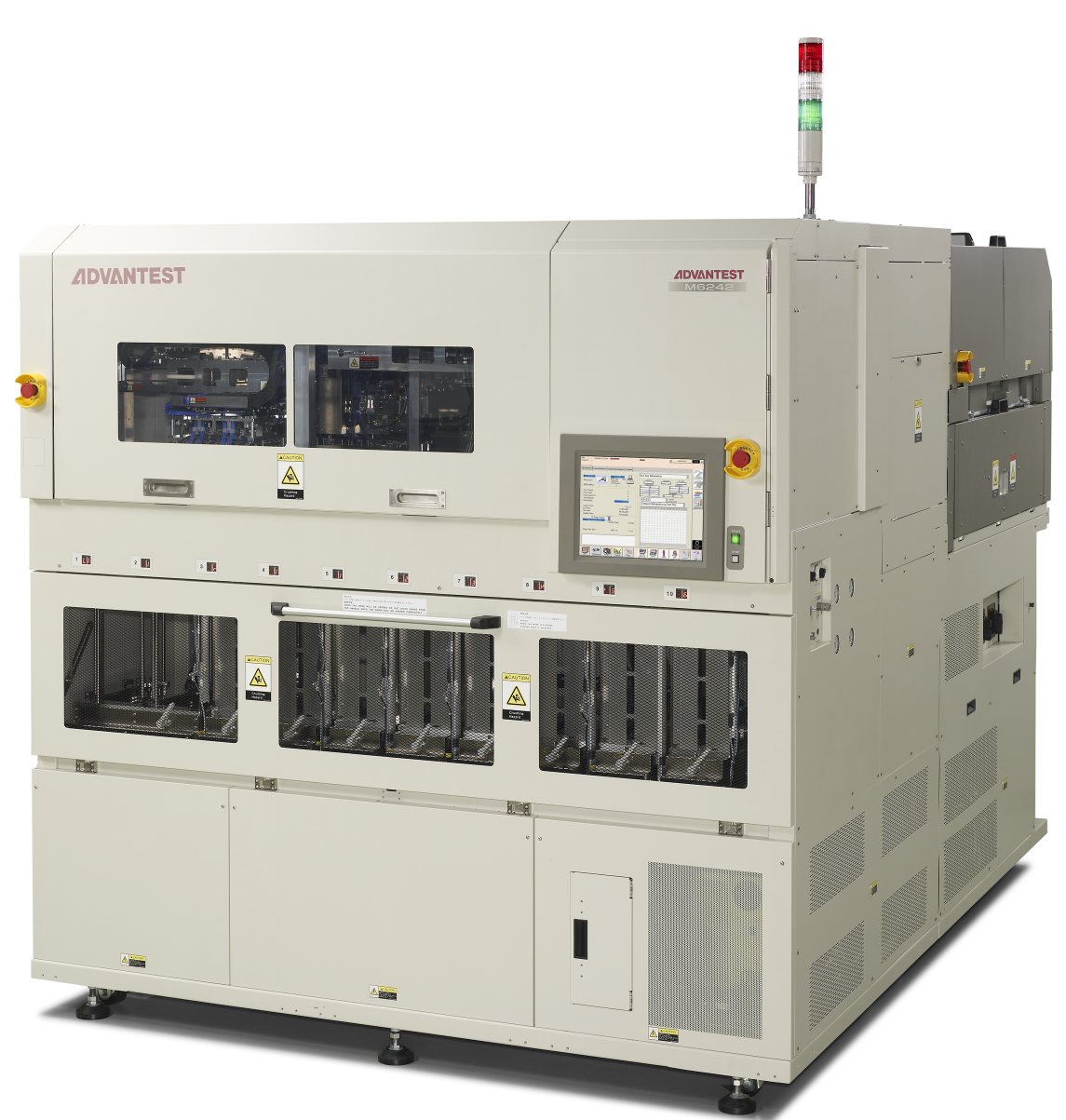
Shown is a memory tester with a workstation and a test head at the left.
This test head can be inserted to the component handler station on the right. Similar test heads are available for a wafer probe station.
Memory testers for charcterization and wafer probing are provided by MOSAID, Advantest and Teradyne.
This test head can be inserted to the component handler station on the right. Similar test heads are available for a wafer probe station.
Memory testers for charcterization and wafer probing are provided by MOSAID, Advantest and Teradyne.
Evaluation platform
|
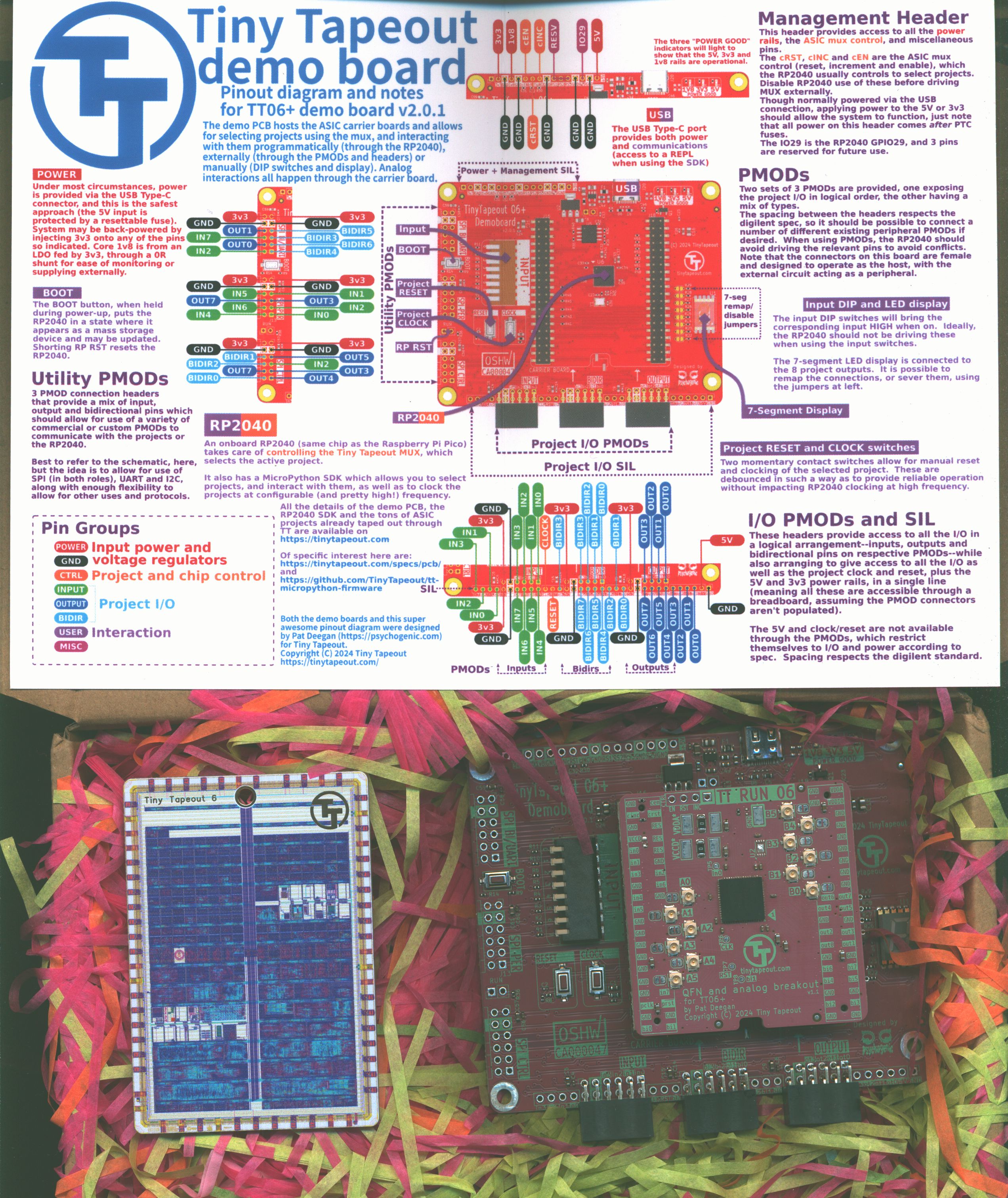
Tiny Tapeout Low cost easy entry chip design 482:1st order passive Sigma Delta ADC Joerg Vollrath https://tinytapeout.com/ |
|
Tiny Tapeout provides an easy way to get from a verilog description
to a digital electronic packaged chip at low cost (200..300.-$ 2025)
in 9 months.
There are 8 digital inputs, 8 digital outputs and 8 digital IOs available.
Additional area and analog pins are provided at higher costs and using a graphical layout tool.
The packaged TinyTapout TT06 chip with evaluation board is pictured on the right.
After cnnecting the board with USB to a PC a design can be selected via a web interface.
Documentation is provided via Github.
There are 8 digital inputs, 8 digital outputs and 8 digital IOs available.
Additional area and analog pins are provided at higher costs and using a graphical layout tool.
The packaged TinyTapout TT06 chip with evaluation board is pictured on the right.
After cnnecting the board with USB to a PC a design can be selected via a web interface.
Documentation is provided via Github.
Test environment
- Input vector
Algorithmic pattern generator (ALPG)
Built in self test (BIST) - DUT
- Output vector
- Interactive Testing
- Test program
Users want to have only working integrating circuits.
During manufacturing a lot can go wrong to cause obvious
and subtle functionality problems.
Test screens bad devices.
Test cost can be up to half of manufacturing costs.
Test is no visible value added. Parts are sorted out as bad and not sellable.
This lecture looks at the area of test.
There is a yearly International Test Conference from the IEEE.
Test screens bad devices.
Test cost can be up to half of manufacturing costs.
Test is no visible value added. Parts are sorted out as bad and not sellable.
This lecture looks at the area of test.
There is a yearly International Test Conference from the IEEE.
Test
- Design for test
- Logic Test
Test vectors - Memory test
Algorithmic pattern generator (ALPG) to test all memory cells - Built in self test (BIST)
Tester on chip - Wafer level test, burn-in test, component test
- Defect oriented versus full test
- Quality, diagnosis
- Boundary scan and JTAG
Motivation:
Minimize test cost and maximize test coverage.
Do I have to test the complete state/truth table?
What is the root cause of a failure?
How can I optimize a process and a design to optimize yield?
Relating defects to fault models and electrical failures!
Minimize test cost and maximize test coverage.
Do I have to test the complete state/truth table?
What is the root cause of a failure?
How can I optimize a process and a design to optimize yield?
Relating defects to fault models and electrical failures!
Yield for Memories
Number of good chips divided by total number of chips
\( Y = \frac{N_{Good}}{N_{Total}} \)
Absolute yield numbers:
- Contact yield: Ycont Equipment and gross fails
- DC Yield YDC: Standby and active current
- Basic functional test (repairable): Screen yield Ys
Write and read all cells - Perfect yield Ys1
Test sequence limited Yield YTSLY
Total yield: Y = Ys*YTSLY
Yield monitors the manufacturing process and ensures good product and maximum profitability.
Number of test
For small logic circuits the whole truth table can be tested.
For large logic circuits the number of input combinations increases exponentially.
Reduction of test vectors using fault models and structural information
Example: NAND
| Nr | IN1 | IN0 | OUT | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | This is tested with vector 1 and 2 and can be omitted |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
For logic circuits basic functionality is ensured testing the state table or truth table.
This can take a lot of time and effort.
This is done in simulation and testing the final product at variuos steps.
VN = 2IN · 2IREG
VN: number of input vectors
IN: number of inputs
IREG: number of registers
Fault Types
- Stuck at fault (SA) “0” or “1” (Logic, array)
short to fixed voltage potentia l - Bridging faults (BF) (Logic, array)
short between lines - Transition faults (TF)
A change of an input is not generating a change in output - Coupling faults (CF) (Array)
short between cells: Write to one cell influences the other cell - Pattern sensitive fault (PSF) (Array)
- RAMs: refresh sensitive faults (Array)
- Timing faults
Defining fault types structures the task of test and yield optimization.
Fault modeling
- Defects: Open, short
- Transistor faults: short between terminals
- Node stuck at faults: '0', '1'
- Transistion delay faults: '0' -> '1', '1' -> '0'
- Truth table based faults
- Path delay faults
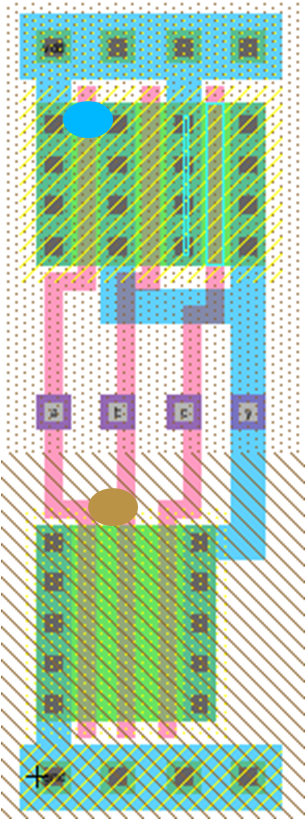
Layout and Defects
The layout influences the probability of shorts caused by defects |
|
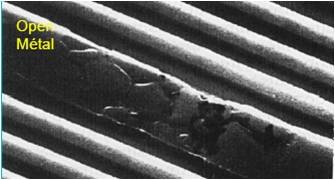
The picture shows a simplified model of defects on a layout.
A remaining metal1 particle shorts the drain and sourc of the upper left PFET.
A polysilicon particle shorts the polysilicon lines of the NFETs from inputs a and b.
A direct short of polysilicon lines from input a and c is not possible without involving polysilicon of input b.
This can have an impact on the necessary test pattern for the inputs.
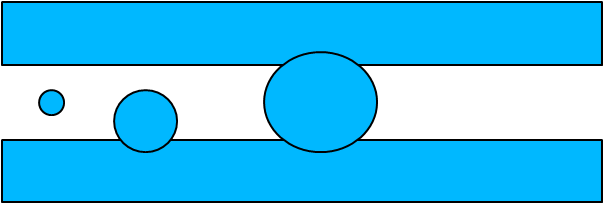
Faults, Layout and Defect size
|
|
Defect wafer map
Same defect count can lead to different signatures
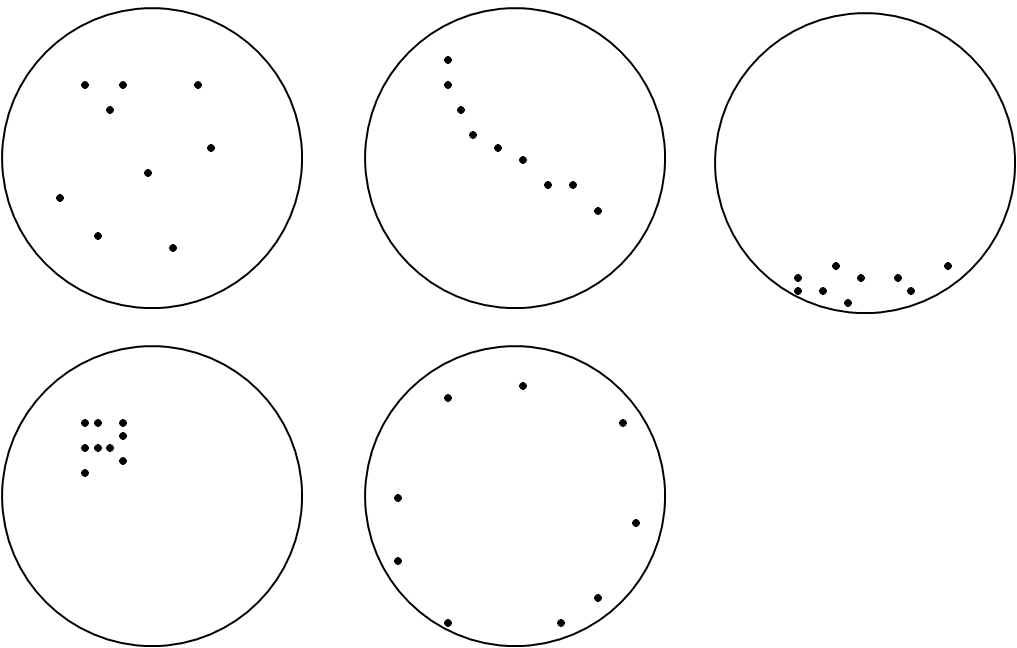
Defects and faults
Defects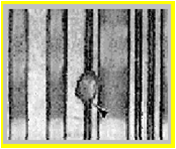
|
|
FaultsS@0 stuck at 0 S@1 stuck at 1 Transition faults (TF) Coupling faults (CF) Realistic fault coverage |
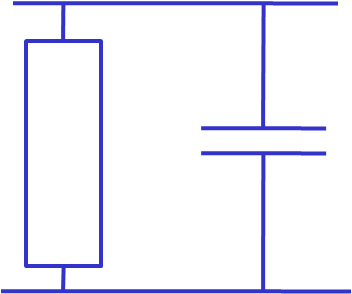
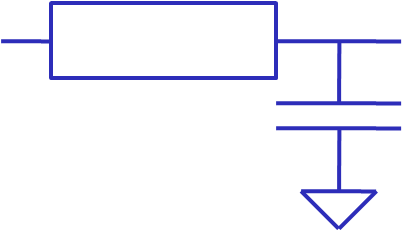
Modeling Defects
|
Hard defects Truth table
|
|

|
Classical Fault Model
Wired-And
|
Dominant
|
Wired-Or
|
A fault between S0 and S1.
A modified truth table for fault modeling is used.
Timing delay fault

Process and Operation point variations
- A CMOS process has some variations
- Lateral dimension
- Layer thickness
- Electrical parameters are influenced
- Therefore SPICE models for worst case are generated
- Low and high Vt MOSFET, short and long channel MOSFET
- A device can be operated at
- Low and high voltage
- Low and high temperature
- Timing simulation has to be done for all worst case operation conditions to ensure functionality
- Process window lots are manufactured to look at process robustness
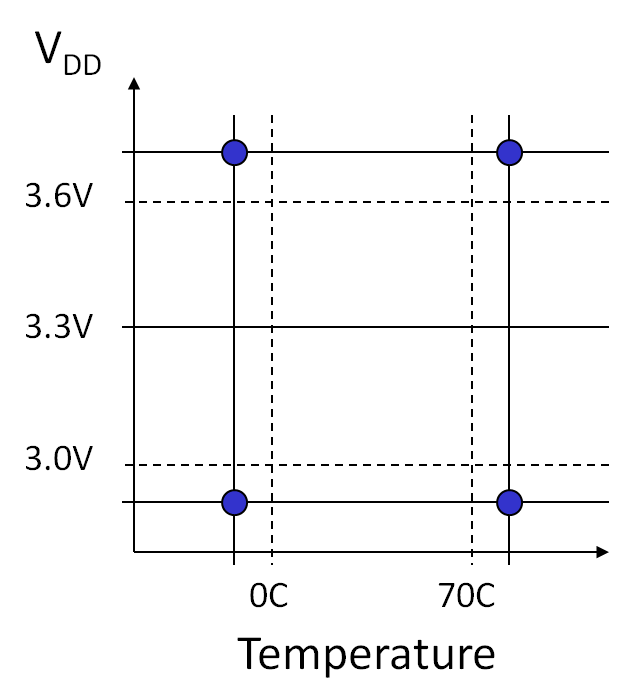
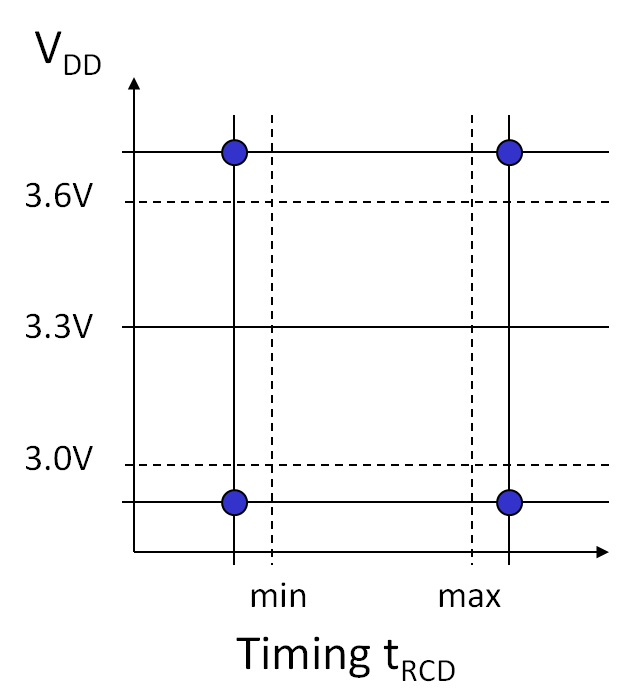
Guard Band
|
|
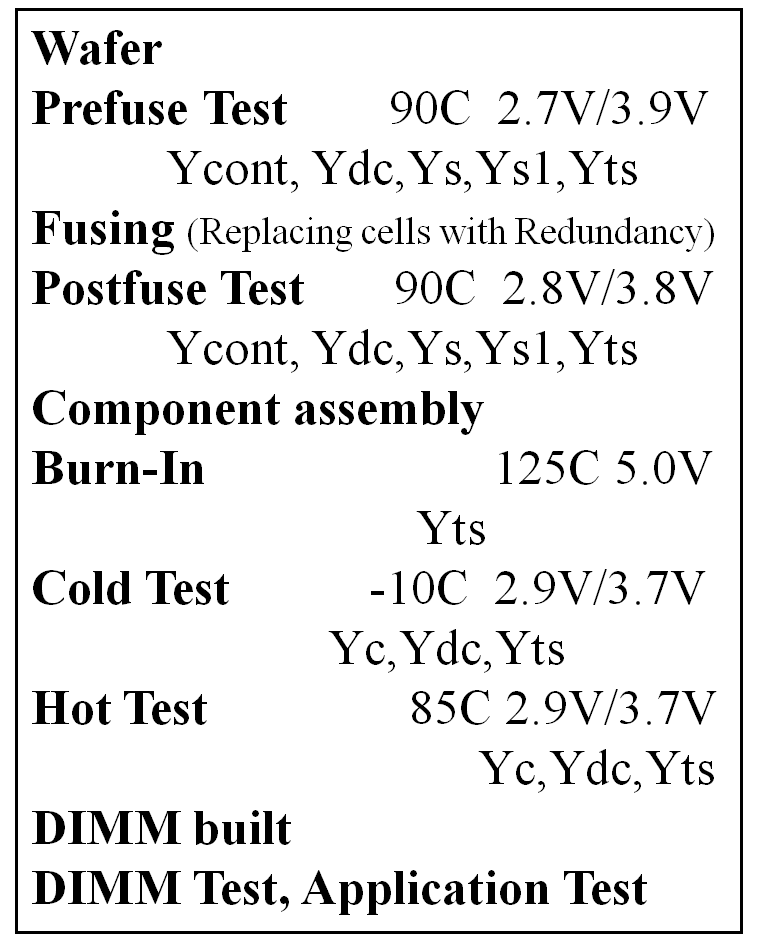
Memory test flow
|
|
Semiconductor Manufacturing
- Development of a new process
Testchip: device optimization
Yield learning
Qualification - Development of a new product
Design: Circuit, pads, test structures
Verification
Qualification - Manufacturing of a new product
Monitoring yield
Root cause analysis
Improvements
Opportunities
Work:
|
Research and Learning
|
Example: Mixed Signal IC (2010)
6 Digital design engineers, 3 analog design engineers, 3 test engineers, 2 support personnel
|
|
Competencies:
|
|