Microelectronics11 MemoryProf. Dr. Jörg VollrathArea, uP, Register, Scan cell |
Video of lecture 11 (16.06.2021)
|
Länge: 1:10:08 |
0:3:45 Picture processing 0:8:0 Examples for memory applications 0:9:56 Memories in personal computers 0:11:30 Memory application 0:20:30 Memory Types 0:22:50 Word line, bit line memory array 0:25:25 Memory array 0:27:17 Memory SRAM LTSPICE schematic 0:30:40 6F2 DRAM manufacturing 0:40:0 SRAM manufacturing 0:49:30 SRAM schematic 0:55:0 Intel: Crosssection showing metal layers different thickness and width 0:56:0 REM picture of SRAM 0:57:20 Feature size and metal pitch 1:0:0 REM picture DRAM 1:2:13 Flash memory 2 TB SSD 1:13:10 Simulation memory operation 1:17:40 DDR3 SDRAM access 1:13:16 Overview remaining lectures, take home test 1:26:0 Typical exam problems |
Overview
Review:- VHDL, VHDL Books
- ASIC, FPGA, Microprocessor
- Delay: Inverter Sizing, Pipeline
Today:
- Area per transistor
- Microprocessor
- Latch, state machine, scan cell
Picture Processing
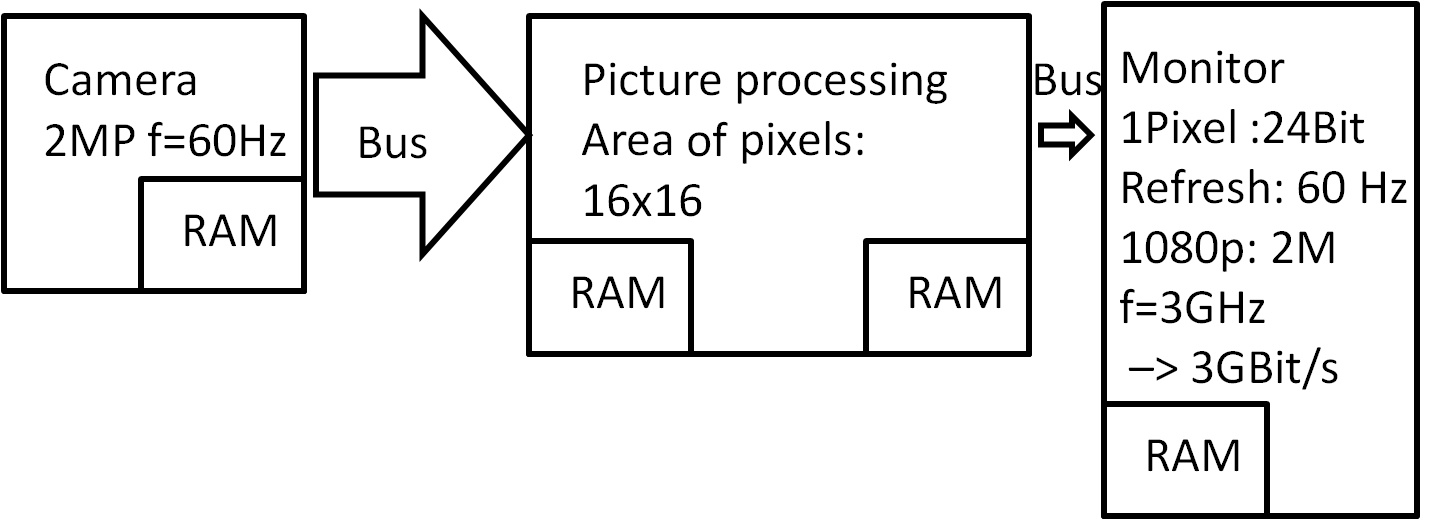
Memories in personal computers
- Bussystem
- Address
- Data
- Controls
- Activate, write, read
Memory: Application
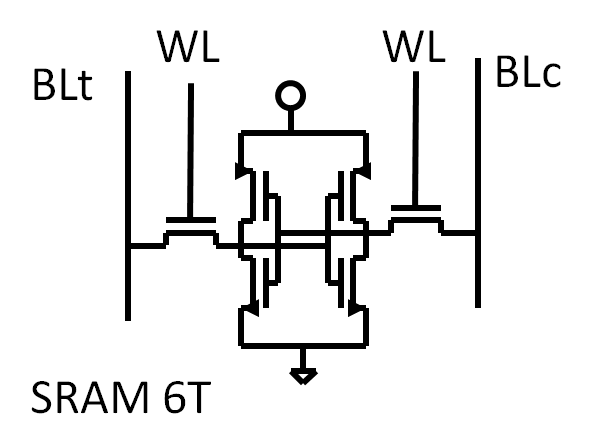
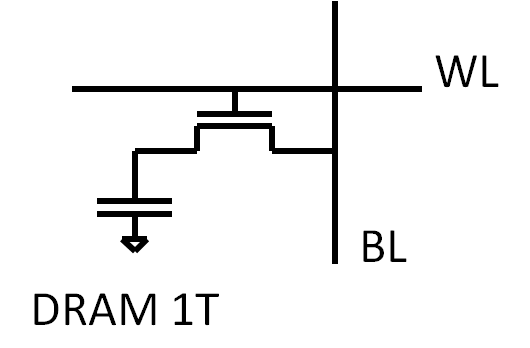
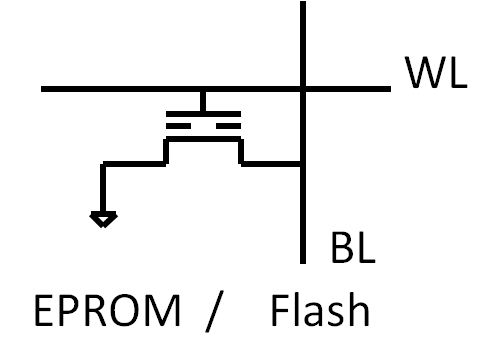
Memory TypesDRAM (capacitor) SRAM (latch of transistors) Flash (transistor with floating gate) FRAM (Ferro Electric hysteresis) MRAM (Resistance change due to magnetization) PCRAM (resistance change due to solid/solid transition)
Needed AreaDRAM: 6F2 one capacitor + 1 select device: 1T + capacitor SRAM: 256F2 4 transistors + 2 select devices: 6 T Flash: 4F2 (16 level: 1F2) 1 Transistor with floating gate: 1T Volatile versus nonvolatile memoriesInformation loss: Volatile versus nonvolatile memories SRAM, DRAM lose information without power, Flash, EPROM and FRAM don’t. DRAM loses information without constant refresh of memory cells. Memory Array
Memory Array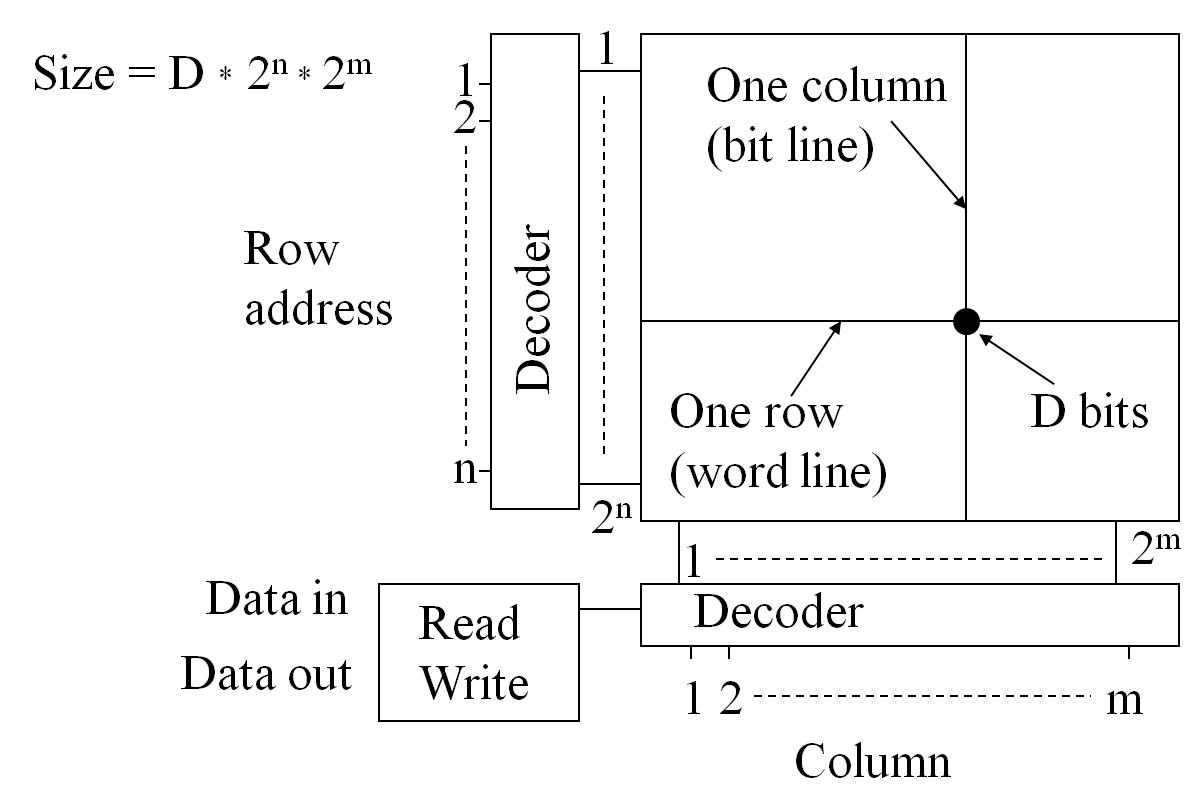
Activation:
Lets analyze a typical DRAM from Micron, Samsung, Hynix. Biggest size DRAM datasheet from Internet. Number of outputs, row address, column address, banks. Intel 14 nm SRAM cellTop view: Cross section: 8
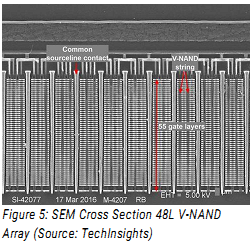
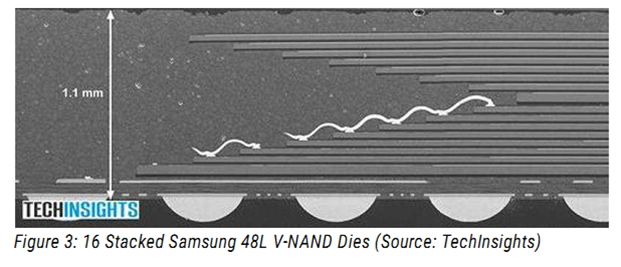
Size: 140 x 364 nm2 = 10 x 26 F2 = 260 F2FINFET: 8nm Width (draw 14 get 8), 42nm FIN pitch, gate pitch 70nm Interconnect pitch 52nm 14nm Intel Core M Processore 1.3 billion Tr. 82 mm2 die size Reference: Intel 14nm technology Samsung 21nm 48L V- 256Gb NAND Flash memory in 2TB SSD
The density is not only determined by F, but by the number of bits ber cell(3) and
vertical integration (48 layers of transistors, 16 dies)
Multiple bits per cell. Multiple cells stacked vertically. Multiple chips per package. More functionality per volume. 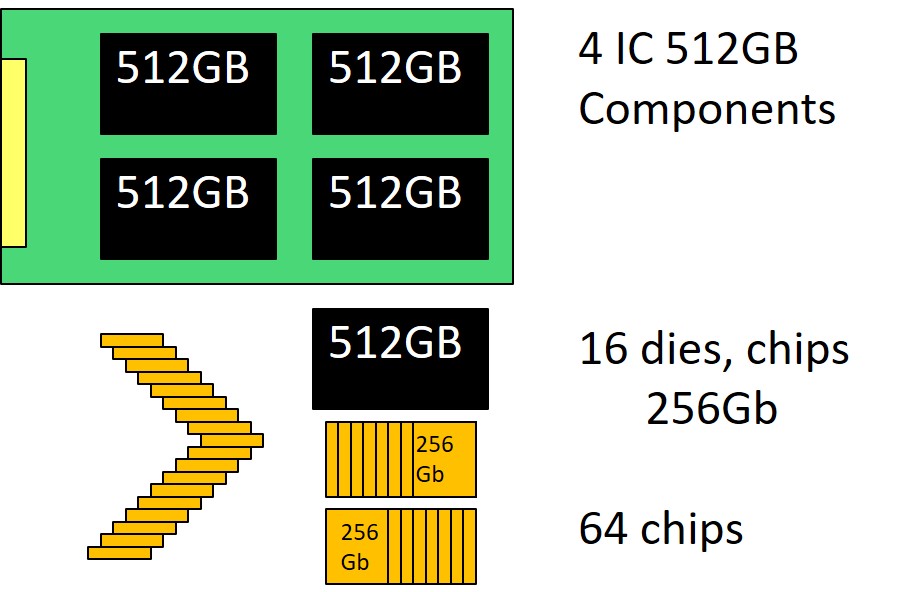
Memory Array SRAM
Positive clock level control
CLK AND (A1, A0) selects a row CLK AND (A2, A3) selects a column WE AND CLK connects DI with data lines Where is the memory cell with address (A3..A0) = "0110"? Which switches are closed with address (A3..A0) = "0110"? Memory cells are connected to BL and BLb. BL and BLb are equalized with CLK='0' Simulation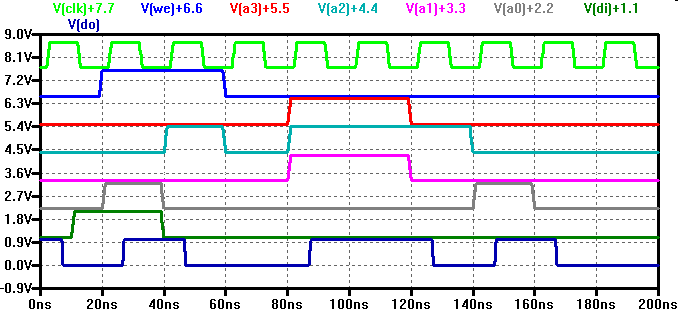
Positive clock level control
Read 0000 '0', Read 0001, Write 0001 ‘1‘, Write 0100 ‘0‘, Read 0000 '0', Read 1110 '1', Read 1110 '1', Read 0100 '0', Read 0001 '1', Read 0000 '0', Read 0000 '0' Delay 10ns from address until data appears VHDL-Code: ROM
VHDL-Code: RAM 01
VHDL-Code: RAM 02
DDR3 SDRAM Access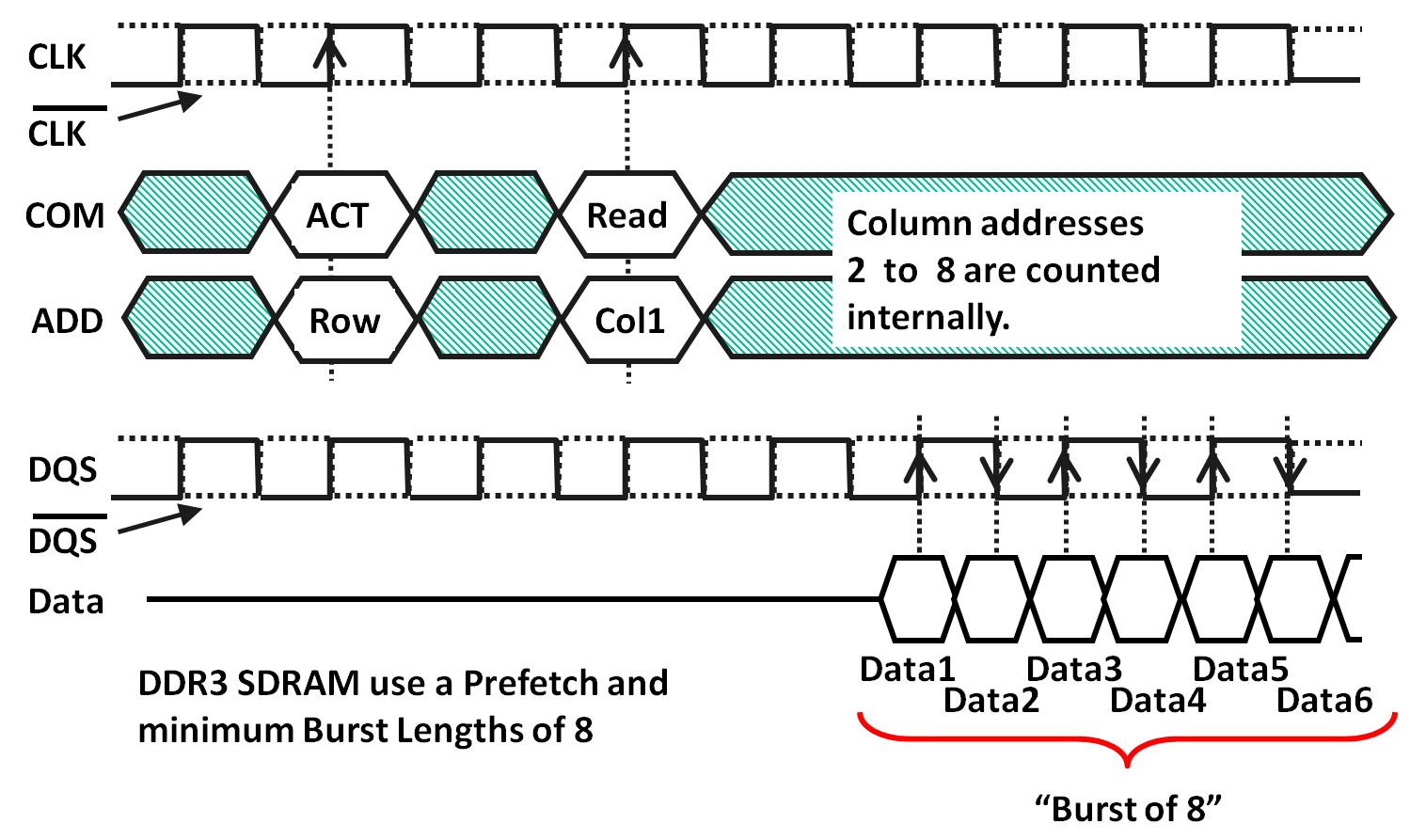
Cycle time:
Latency: Summary
Next: 12 Power, Clock, Input, Output (IO) Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften Kempten, Jörg Vollrath, Bahnhofstraße 61 · 87435 Kempten Tel. 0831/25 23-0 · Fax 0831/25 23-104 · E-Mail: joerg.vollrath(at)hs-kempten.de Impressum
|